使用MutationObserver 与 IntersectionObserver来监听页面元素
- 2020.05.13
场景
实际业务开发中常常会遇到滚动到顶部或者tab初始为相对定位,滚动一段距离后切换为fixed定位的场景,tab下往往是一些tabList。一个比较友好的交互是当用户在切换tab的时候,可以自动的定位到对应tab下的list的初始位置。
初始版本
为了满足上面描述的业务场景,我们先来实现一个简单版本的效果
<Page>
<Content1 />
<Sticky>
<Tab />
<Sticky>
<TabList />
</Page>
假设我们的页面结构就是这样组成的,其中Sticky组件表示滚动到指定位置后Tab组件会变成fixed定位。
- 2020.05.14
使用ScrollIntoView
Element.scrollIntoView()让当前的元素滚动到浏览器窗口的可视区域内。
语法
element.scrollIntoView();// 等同于element.scrollIntoView(true)
element.scrollIntoView(true);// 元素的顶端将和其所在滚动区的可视区域的顶端对齐。相应的 scrollIntoViewOptions: {block: "start", inline: "nearest"}。这是这个参数的默认值。
element.scrollIntoView(false);// 元素的底端将和其所在滚动区的可视区域的底端对齐。相应的scrollIntoViewOptions: {block: "end", inline: "nearest"}。
element.scrollIntoView(scrollIntoViewOptions);
scrollIntoViewOptions
| 参数名 | 参数形式 | 参数描述 |
|---|---|---|
| behavior | 可选 | 定义动画过渡效果, "auto"`或 "smooth" 之一。默认为 "auto"。 |
| block | 可选 | 定义垂直方向的对齐, "start", "center", "end", 或 "nearest"之一。默认为 "start"。 |
| inline | 可选 | 定义水平方向的对齐, "start", "center", "end", 或 "nearest"之一。默认为 "nearest"。 |
这个是H5上用来滚动元素到指定位置的方法.
WARNING
很不幸,这是一个实验中的功能.
而且在实际的使用过程中,由于我们的tab是fixed定位的,我们让tabList执行scrollIntoView()方法后部门内容会被tab遮挡。只能另寻他法。
所以假如有fixed布局的元素的时候使用此方法并不能达到滚动到顶部的效果。
使用scrollTo
window.scrollTo(xPos, yPos, behavior:[smooth, instant]);
既然scrollIntoView方法不能满足我们的需求 那我们就用原始的scrollTo方法来实现吧。
还是上面的代码。
const id = tabList.id;// 获取到对应tabList元素的id
const top = document.querySelector(`#${id}`).offSetTop; // 获取到元素的offsetTop
window.scrollTo(top, { behavior: 'smooth');
WARNING
的确,使用这个方法可以解决我们的问题,但是在后来场景的应用中产生了另外一个问题。
由于项目中的列表用的是懒加载组件,恰好监听的是scroll方法,这时当我们滚动到列表底部 然后切换tab的时候,视窗会滚动到列表的初始位置,但是下方的所有listItem都会重新去请求,造成了很多不必要的请求。
使用MutationObserver
MutationObserver接口提供了监视对DOM树所做更改的能力。它被设计为旧的Mutation Events功能的替代品,该功能是DOM3 Events规范的一部分。
支持情况
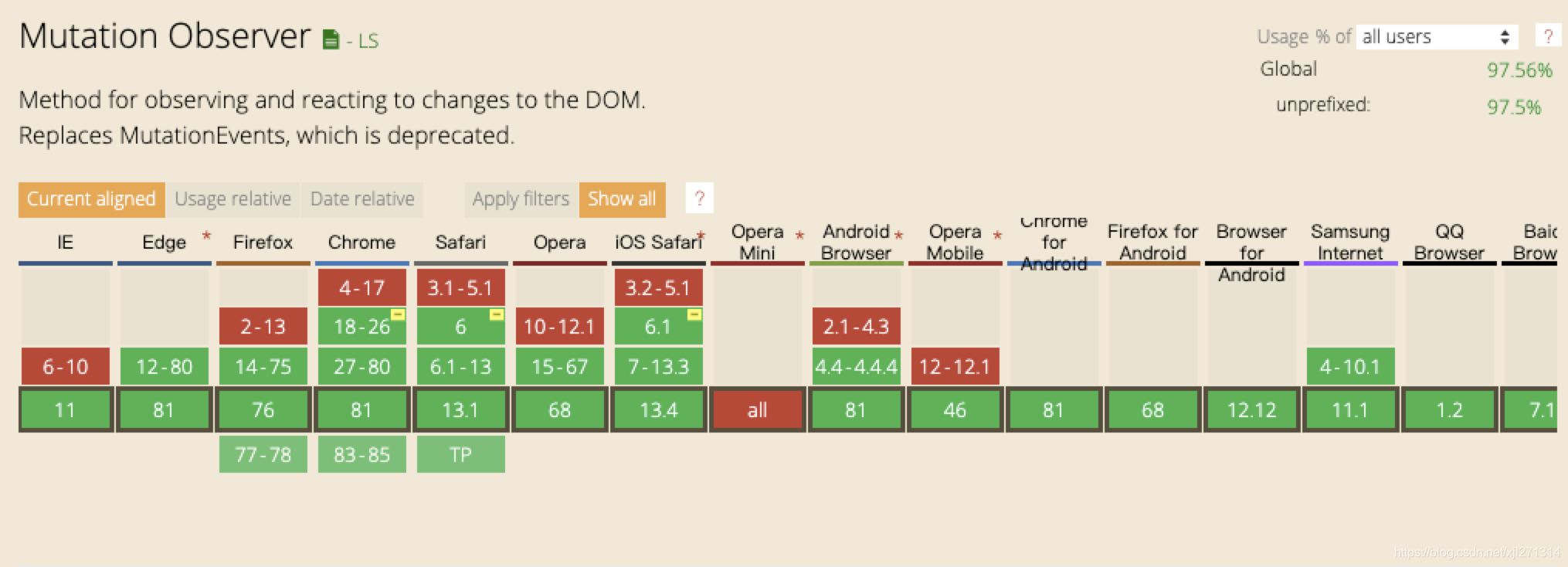
语法
构造函数
MutationObserver():创建并返回一个新的MutationObserver它会在指定的DOM发生变化时被调用。
方法
disconnect():阻止MutationObserver实例继续接收的通知,直到再次调用其observe()方法,该观察者对象包含的回调函数都不会再被调用。
observe(target, options):接受两个参数,一个是监听的对象(target),一个是观察的选项(options)。
takeRecords():清空监听的队列,并返回结果。
执行逻辑
- 先执行监听的微任务队列;
- 执行完微任务队列之后就把所监听的记录封装成一个数组来处理;
- 然后返回处理结果。
参数说明
options可选参数如下:
| 参数名 | 参数描述 |
|---|---|
| childList | 监听目标子节点的变化。 |
| attributes | 监听目标属性的变化。 |
| characterData | 监听目标数据的变化。 |
| subtree | 监听目标以及其后代的变化。 |
| attributeOldValue | 监听目标属性变化前的具体值。 |
| characterDataOldValue | 监听目标数据变化前的具体值。 |
| attributeFilter | 不需要监听的属性列表(此属性填入过滤的属性列表)。 |
示例
// Select the node that will be observed for mutations
var targetNode = document.getElementById('some-id');
// Options for the observer (which mutations to observe)
var config = { attributes: true, childList: true, subtree: true };
// Callback function to execute when mutations are observed
var callback = function(mutationsList) {
for(var mutation of mutationsList) {
if (mutation.type == 'childList') {
console.log('A child node has been added or removed.');
}
else if (mutation.type == 'attributes') {
console.log('The ' + mutation.attributeName + ' attribute was modified.');
}
}
};
// Create an observer instance linked to the callback function
var observer = new MutationObserver(callback);
// Start observing the target node for configured mutations
observer.observe(targetNode, config);
// Later, you can stop observing
observer.disconnect();
简单应用
export function debounce(fn, waitTime = 450) {
let timeout;
return function () {
clearTimeout(timeout);
const args = arguments;
timeout = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, [...args]);
}, waitTime);
};
}
const config = { attributes: true, childList: true, subtree: true };
export default function observeNode(targetNode, callback) {
// Create an observer instance linked to the callback function
const MutationObserver = window.MutationObserver || window.WebKitMutationObserver || window.MozMutationObserver;
const observer = new MutationObserver(callback);
// Start observing the target node for configured mutations
observer.observe(targetNode, config);
const realFn = debounce(callback, 400);
window.addEventListener('resize', realFn);
// Later, you can stop observing
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('resize', realFn);
observer.disconnect();
};
}
- 2020.05.15
Intersection Observer
IntersectionObserver接口(从属于Intersection Observer API)为开发者提供了一种可以异步监听目标元素与其祖先或视窗(viewport)交叉状态的手段。祖先元素与视窗(viewport)被称为根(root)。
简单的说这个API就是用来观察元素是否在视窗内等场景。
语法
const io = new IntersectionObserver(callback, options)
IntersectionObserver是浏览器原生提供的构造函数,接受两个参数:callback是可见性变化时的回调函数,option是配置对象(该参数可选)。
方法
IntersectionObserver.observe():开始监听;
IntersectionObserver.disconnect():停止监听;
IntersectionObserver.unobserve(target):使IntersectionObserver停止监听特定目标元素。
参数说明
callback
当元素的可见性变化时,就会触发
callback函数。callback函数会触发两次,元素进入视窗(开始可见时)和元素离开视窗(开始不可见时)都会触发。var io = new IntersectionObserver((entries)=>{ console.log(entries) }) io.observe(target)callback函数有个entries参数,它是个IntersectionObserverEntry对象数组,接下来我们重点说下IntersectionObserverEntry对象。boundingClientRect
目标元素的矩形信息
intersectionRatio
相交区域和目标元素的比例值
intersectionRect/boundingClientRect不可见时小于等于0intersectionRect
目标元素和视窗(根)相交的矩形信息 可以称为相交区域
isIntersecting
目标元素当前是否可见 Boolean值 可见为true
rootBounds
根元素的矩形信息,没有指定根元素就是当前视窗的矩形信息
target
观察的目标元素
time
返回一个记录从IntersectionObserver的时间到交叉被触发的时间的时间戳
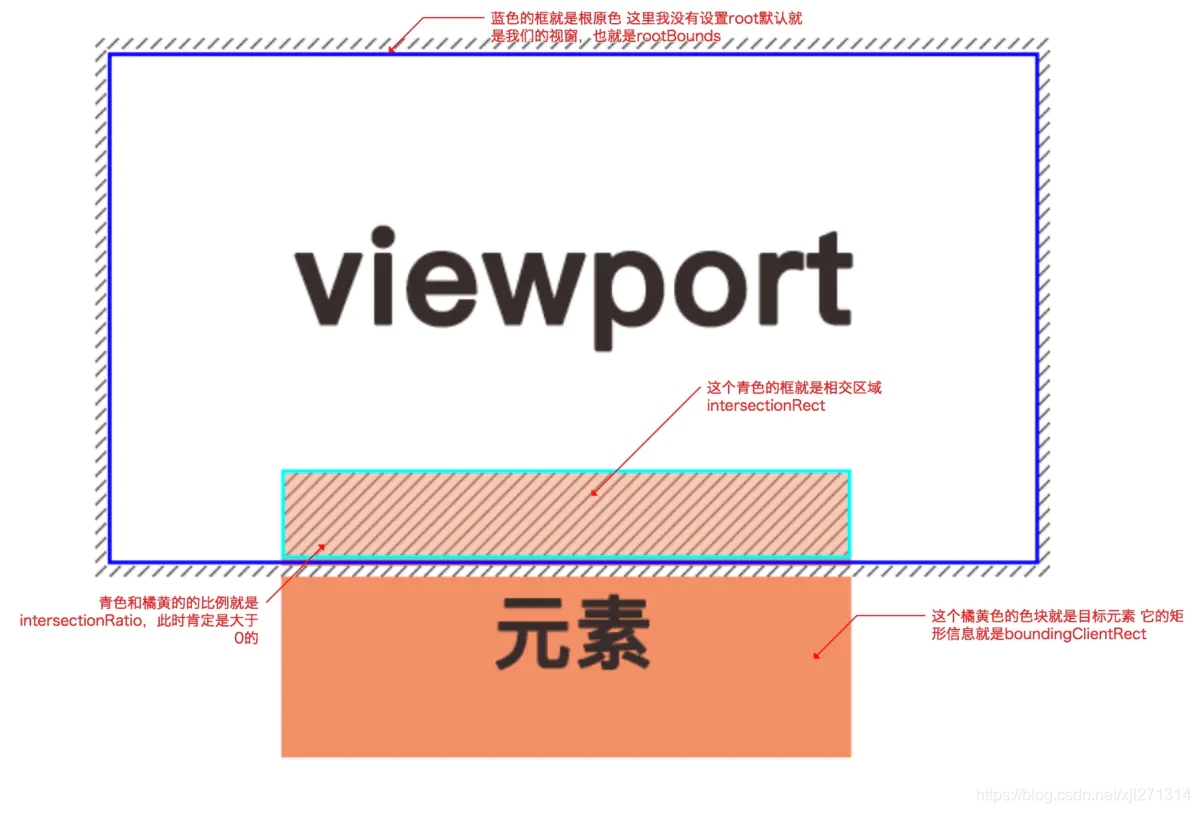
options
root
用于观察的根元素,默认是浏览器的视口,也可以指定具体元素,指定元素的时候用于观察的元素必须是指定元素的子元素
threshold
用来指定交叉比例,决定什么时候触发回调函数,是一个数组,默认是[0]。
const options = { root: null, threshold: [0, 0.5, 1] } var io = new IntersectionObserver(callback, options) io.observe(document.querySelector('img'))上面代码,我们指定了交叉比例为0,0.5,1,当观察元素img0%、50%、100%时候就会触发回调函数
rootMargin
用来扩大或者缩小视窗的的大小,使用css的定义方法,10px 10px 30px 20px表示top、right、bottom 和 left的值
const options = { root: document.querySelector('.box'), threshold: [0, 0.5, 1], rootMargin: '30px 100px 20px' }
实际应用
根据这个API的功能经常用于图片懒加载的功能实现,话不多说直接上代码。
const io = new IntersectionObserver(()=>{ // 实例化 默认基于当前视窗
})
let imgSrc = document.querySelectorAll('[data-src]') // 将图片的真实url设置为data-src src属性为占位图 元素可见时候替换src
function callback(entries){
entries.forEach((item) => { // 遍历entries数组
if(item.isIntersecting){ // 当前元素可见
item.target.src = item.target.dataset.src // 替换src
io.unobserve(item.target) // 停止观察当前元素 避免不可见时候再次调用callback函数
}
})
}
imgSrc.forEach((item)=>{ // io.observe接受一个DOM元素,添加多个监听 使用forEach
io.observe(item)
})
WARNING
IntersectionObserver()的实现和requestIdleCallback()API一致,即只有线程空闲下来,才会执行观察器。这意味着,这个观察器的优先级非常低,只在其他任务执行完,浏览器有了空闲才会执行。
← 奇淫技巧 Javascript设计模式详解 →