webpack
本文所阐述的相关知识都是基于 webpack4.x 版本
定义
webpack是一个现代JavasScript应用程序的模块打包器(module bunder)
四个核心概念
入口(entry)输出(output)loader插件(plugins)
入口
指示
webpack应该使用哪个模块,来作为构建其内部依赖图的开始。Webpack 执行构建的第一步将从 入口开始,搜寻及递归解析出所有入口依赖的模块。
// 最简单的单入口文件
module.exports = {
entry: "./path/to/my/entry/file.js",
};
// entry 属性的单个入口语法,是下面的简写:
const config = {
entry: {
main: "./path/to/my/entry/file.js",
},
};
module.exports = config;
出口
output属性告诉webpack在哪里输出它所创建的bundles,以及如何命名这些文件,默认值为./dist。基本上,整个应用程序结构,都会被编译到你指定的输出路径的文件夹中。你可以通过在配置中指定一个output字段,来配置这些处理过程:
// 简单的单入口 单出口配置
const path = require("path");
module.exports = {
entry: "./path/to/my/entry/file.js",
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "dist"),
filename: "my-first-webpack.bundle.js",
},
};
loader
loader让webpack能够去处理那些非JavaScript文件(webpack自身只理解JavaScript)。loader可以将所有类型的文件转换为webpack能够处理的有效模块,然后你就可以利用webpack的打包能力,对它们进行处理。
本质上,webpack loader 将所有类型的文件,转换为应用程序的依赖图(和最终的 bundle)可以直接引用的模块。
TIP
在 webpack 的配置中 loader 有两个目标:
test属性,用于标识出应该被对应的loader进行转换的某个或某些文件。use属性,表示进行转换时,应该使用哪个loader。
thread-loader:可以配置 webpack 进行多进程的打包 js 和 css。
// 简单的loader配置
const path = require("path");
const config = {
output: {
filename: "my-first-webpack.bundle.js",
},
module: {
rules: [
{ test: /\.txt$/, use: "raw-loader" },
{
test: /\.js$/, //匹配所有的js文件
exclude: /node_modules/, //除了node_modules以外
},
// 配置css loaders 假如在index.js中引入css 会被转化成commonjs对象
{ test: /\.css$/, use: ["style-loader", "css-loader"] },
// styles-loader 将css转化成style 插入到head中
{ test: /\.less$/, use: ["style-loader", "css-loader", "less-loader"] },
{ test: /\.scss$/, use: ["style-loader", "css-loader", "sass-loader"] },
// url-loader可以处理一些图片大小转base64的功能 limit的单位是B(字节)
{
test: /\.png|jpg|jpeg|gif$/,
use: [(loader: "url-loader"), (options: { limit: 10240 })],
},
],
},
};
module.exports = config;
loader 特性
loader 支持链式传递。能够对资源使用流水线(pipeline)。一组链式的 loader 将按照相反的顺序执行。loader 链中的第一个 loader 返回值给下一个 loader。在最后一个 loader,返回 webpack 所预期的 JavaScript。
loader 可以是同步的,也可以是异步的。
loader 运行在 Node.js 中,并且能够执行任何可能的操作。
loader 接收查询参数。用于对 loader 传递配置。
loader 也能够使用 options 对象进行配置。
除了使用 package.json 常见的 main 属性,还可以将普通的 npm 模块导出为 loader,做法是在 package.json 里定义一个 loader 字段。
插件(plugin)可以为 loader 带来更多特性。
loader 能够产生额外的任意文件。
插件(plugins)
loader被用于转换某些类型的模块,而插件则可以用于执行范围更广的任务。插件的范围包括,从打包优化和压缩,一直到重新定义环境中的变量。插件接口功能极其强大,可以用来处理各种各样的任务。
想要使用一个插件,你只需要 require() 它,然后把它添加到 plugins 数组中。多数插件可以通过选项(option)自定义。你也可以在一个配置文件中因为不同目的而多次使用同一个插件,这时需要通过使用 new 操作符来创建它的一个实例。
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require("html-webpack-plugin"); // 通过 npm 安装
const webpack = require("webpack"); // 用于访问内置插件
const config = {
module: {
rules: [{ test: /\.txt$/, use: "raw-loader" }],
},
plugins: [new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ template: "./src/index.html" })],
};
module.exports = config;
TIP
webpack 提供许多开箱可用的插件!查阅插件列表获取更多信息。
模式(mode)
webpack内置了两个不同的模式(development、production),通过选择development或production之中的一个,来设置mode参数,你可以启用相应模式下的webpack内置的优化。
- development模式下,将侧重于功能调试和优化开发体验,包含如下内容:
- 浏览器调试工具
- 开发阶段的详细错误日志和提示
- 快速和优化的增量构建机制
- production模式下,将侧重于模块体积优化和线上部署,包含如下内容:
- 开启所有的优化代码
- 更小的
bundle大小 - 去除掉只在开发阶段运行的代码
Scope hoisting和Tree-shaking- 自动启用
uglifyjs对代码进行压缩
manifest
在使用 webpack 构建的典型应用程序或站点中,有三种主要的代码类型:
- 你或你的团队编写的源码。
- 你的源码会依赖的任何第三方的 library 或 "vendor" 代码。
- webpack 的
runtime和manifest,管理所有模块的交互。
Runtime
如上所述,我们这里只简略地介绍一下。runtime,以及伴随的 manifest 数据,主要是指:在浏览器运行时,webpack 用来连接模块化的应用程序的所有代码。runtime 包含:在模块交互时,连接模块所需的加载和解析逻辑。包括浏览器中的已加载模块的连接,以及懒加载模块的执行逻辑。
Manifest 那么,一旦你的应用程序中,形如 index.html 文件、一些 bundle 和各种资源加载到浏览器中,会发生什么?你精心安排的 /src 目录的文件结构现在已经不存在,所以 webpack 如何管理所有模块之间的交互呢?这就是 manifest 数据用途的由来……
当编译器(compiler)开始执行、解析和映射应用程序时,它会保留所有模块的详细要点。这个数据集合称为 "Manifest",当完成打包并发送到浏览器时,会在运行时通过 Manifest 来解析和加载模块。无论你选择哪种模块语法,那些 import 或 require 语句现在都已经转换为 webpack_require 方法,此方法指向模块标识符(module identifier)。通过使用 manifest 中的数据,runtime 将能够查询模块标识符,检索出背后对应的模块。
模块热替换
模块热替换(HMR - Hot Module Replacement)功能会在应用程序运行过程中替换、添加或删除模块,而无需重新加载整个页面。主要是通过以下几种方式,来显著加快开发速度:
保留在完全重新加载页面时丢失的应用程序状态。
只更新变更内容,以节省宝贵的开发时间。
调整样式更加快速 - 几乎相当于在浏览器调试器中更改样式。
你可以设置 HMR,以使此进程自动触发更新,或者你可以选择要求在用户交互时进行更新。通常我们可以使用webpack-dev-server来进行处理。
TIP
webpack-dev-server不会刷新浏览器webpack-dev-server不输出文件,二是放在内存中使用
HotModuleReplacementPlugin插件(webpack 自带)使用
webpack-dev-middleware也可以实现相同的功能,不过这种方式会将webpack输出的文件传输给服务器,适用于灵活的定制场景。
热更新原理
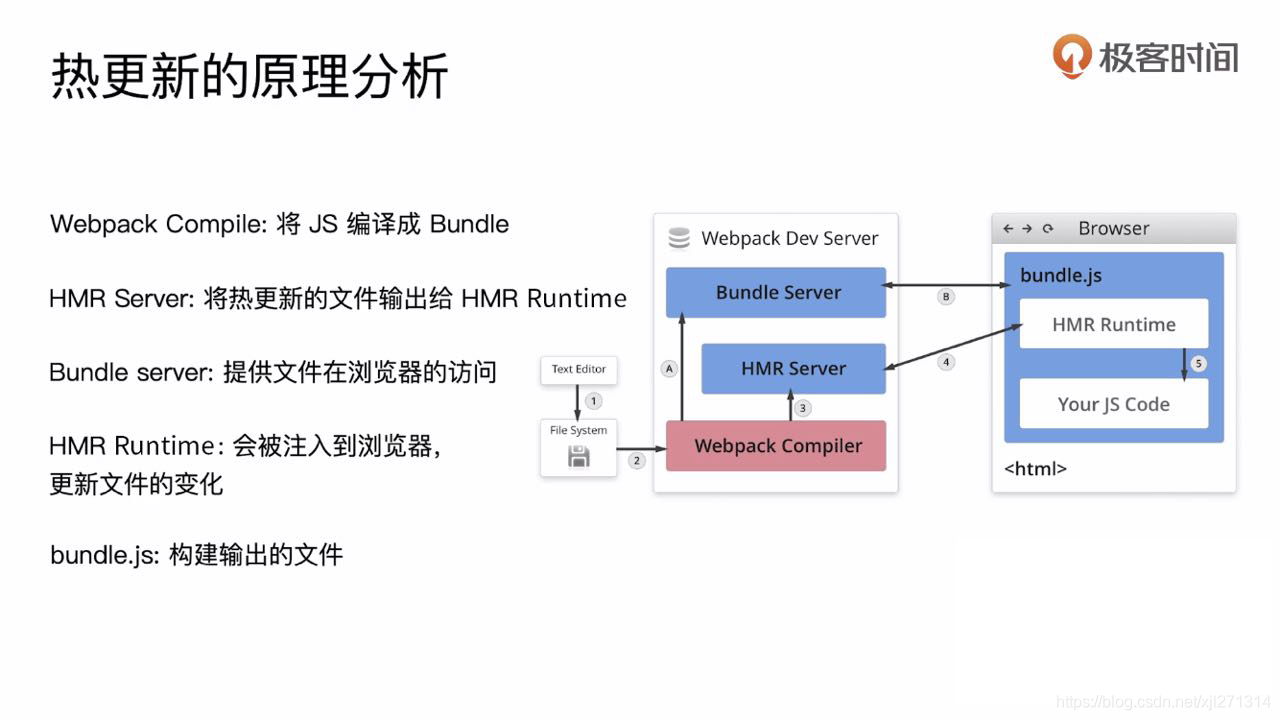
文件监听
文件监听是在发现源码发生变化的时候,自动的构建出新的输出文件。
webpack 中开启监听模式有两种方式实现:
启动
webpack的时候带上--watch参数在配置
webpack.config.js的时候设置watch:true
WARNING
这种方式虽然 webpack 构建是成功了 但是需要开发者手动刷新浏览器才会显示效果
文件监听的原理
轮询的判断文件的最后编辑时间是否发生了变化。当某个文件发生了变化,并不会立即告诉监听者,而是先缓存起来,等待
aggregateTimeout
modules.exports = {
// 默认是false 不开启
watch: true,
// 只有watch开启之后才会有效
watchOptions: {
// 默认为空 不监听的文件或文件夹 支持正则匹配
ignored: /node_modules/,
// 监听到变化后等待多少ms之后执行 默认是300ms
aggregateTimeout: 300,
// 判断文件是否发生变化通过不停询问系统指定文件有没有变化实现的, 默认为每秒询问1000次
poll: 1000,
},
};
文件指纹
文件指纹其实指的就是每次文件打包之后后面跟着的
HashCode,用来做版本管理等功能
分类
Hash: 和整个项目的构建有关,只要项目文件有修改,整个项目构建的 hash 值就会更改。Chunkhash: 和webpack打包的chunk有关,不同的entry会生成不同的chunkhash。Contenthash: 根据文件的内容来定义hash,文件内容不变,则contenthash不变。
自动清理构建目录
- 2020.05.18
默认情况下每次 webpack 的构建的需要手动去清除之前构建产生的目录文件,这样在实际工程中就变得很麻烦。下面将会讲解几种自动化清理构建目录的方法。
- 通过 script 命令
rm -rf ./dist && webpack
// rimraf 是个插件库
rimraf ./dist && webpack
- 使用
clean-webpack-plugin插件
这个插件默认会删除
output指定的输出目录
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin();
]
CSS 增强
1. 自动补全属性兼容
CSS3 某些属性其实在不同浏览器的支持情况不一样,以前的 css 代码中经常会出现以下这种 qingx
-moz-border-redius: 50px;
-webkit-border-redius: 50px;
-o-border-redius: 50px;
-ms-border-redius: 50px;
border-redius: 50px;
如何只编写 W3C 规范的属性,其余的让大宝工具自动帮助我们完成?
其实我们可以通过使用post-css和autoprefixer插件来辅助我们完成这个功能。
module.exports = {
...,
module: {
rule: [{
test: /\.scss$/,
use: [{
loader: require.resolve('style-loader')
},
{
loader: require.resolve('css-loader')
},
{
loader: require.resolve('postcss-loader'),
options: {
plugins: [
require('autoprefixer')({
overrideBrowserslist: ['last 4 versions', 'ie 9', 'android 4.4.4', 'ios 8'],
}),
],
},
},
{
loader: require.resolve('sass-loader'),
options: {
modifyVars: true,
javascriptEnabled: true
},
},
],
}, ]
}
}
机制是在 CanIUse 上查找兼容性。
2. 自动 px 转 rem 适配移动端
const {
addPostcssPlugins,
} = require("customize-cra");
addPostcssPlugins([require('postcss-px2rem')({ remUnit: 75 / 2 })]), // px转换成rem
// 早期版本
module.exports ={
...,
{
loader: 'px2rem-loader',
options: {
remUnit: 75,// 1rem = 75px 750设计稿
remPrecision: 8 ,// px转rem小数点位数
}
},
}
TIP
推荐使用手机淘宝的lib-flexible库配套使用 或者使用本博客对应的 js 技巧篇中的方法。
静态资源内联
意义
页面框架的初始化脚本
上报相关打点
CSS 内联避免页面闪动
小图片或者字体内联 减少
HTTP请求数
实现
主要是用 raw-loader来实现静态资源内联。
功能
raw-loader内联 html
<script>${require("raw-loader!babel-loader!./meta.html")}</script>
raw-loader内联 js
<script>
${require("raw-loader!babel-loader!../node_modules/lib_flexible")}
</script>
实现 css 内联
- 借助
style-loader
module.exports = {
...,
{
loader: 'style-loader',
options:{
insertAt: 'top',// 样式插入head
singleton: true, // 将所有的style标签合并成一个
}
}
}
- 使用
html-inline-css-webpack-plugin
使用 source map
soure map 可以将打包后的文件与原文件建立映射 方便查找打包之前的文件、定位错误
WARNING
注意: 一般仅在开发环境开启
关键字
eval: 使用eval包裹模块代码source map: 产生.map文件cheap: 不包含列信息inline: 将.map作为DataURI嵌入,不单独生成.map文件module: 包含loader的sourcemap
提取页面的公共资源
基础库的分离
将 react、react-dom 等基础包通过 cdn 引入,不打入 bundle 中。
实际操作起来就是将这些库使用externals进行引入或者使用splitChunks进行分割.
使用 html-webpack-externals-plugin
// 安装
npm i html-webpack-externals-plugin -D
// 使用
const HtmlWebpackExternalsPlugin = require('html-webpack-externals-plugin');
module.exports = {
...,
plugins: [
...,
new HtmlWebpackExternalsPlugin({
externals: [
{
module: 'react',
entry: 'cdn文件地址',
global: 'React'
},
{
module: 'react-dom',
entry: 'cdn文件地址',
global: 'ReactDOM'
}
]
})
]
}
// index.html
<script src="依赖地址"></script>
splitChunks
- 2020.05.18
splitChunks算是webpack中比较高级的一个用法,主要是跟模块拆分与代码拆分功能相关。
在研究splitChunks之前,我们先再回顾下webpack中的module、chunk和bundle。
module:就是 js 的模块化webpack支持commonJS、ES6等模块化规范,简单来说就是你通过import语句引入的代码。chunk:chunk是webpack根据功能拆分出来的,包含三种情况:- 你的项目入口
(entry) - 通过
import()动态引入的代码 - 通过
splitChunks拆分出来的代码
- 你的项目入口
chunk包含着module,可能是一对多也可能是一对一。
bundle:bundle是webpack打包之后的各个文件,一般就是和chunk是一对一的关系,bundle就是对chunk进行编译压缩打包等处理之后的产出。
在webpack4之后有一个默认的splitChunks配置:
module.exports = {
//...
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
chunks: "async",
minSize: 30000,
minChunks: 1,
maxAsyncRequests: 5,
maxInitialRequests: 3,
automaticNameDelimiter: "~",
name: true,
cacheGroups: {
vendors: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/,
priority: -10,
},
default: {
minChunks: 2,
priority: -20,
reuseExistingChunk: true,
},
},
},
},
};
chunks
chunks的含义是拆分模块的范围,它有三个值async、initial和all。
async表示只从异步加载得模块(动态加载import())里面进行拆分initial表示只从入口模块进行拆分all表示以上两者都包括
chunks的默认配置是async,也就是只从动态加载得模块里面进行拆分
cacheGroups
cacheGroups其实是splitChunks里面最核心的配置,splitChunks就是根据cacheGroups去拆分模块的.
splitChunks默认有两个缓存组:vender和default。
如果有一个模块满足了多个缓存组的条件就会去按照权重划分,谁的权重高就优先按照谁的规则处理。
maxInitialRequests
表示允许入口并行加载的最大请求数。
之所以有这个配置也是为了对拆分数量进行限制,不至于拆分出太多模块导致请求数量过多而得不偿失。
这里需要注意几点:
- 入口文件本身算一个请求
- 如果入口里面有动态加载得模块这个不算在内
- 通过
runtimeChunk拆分出的runtime不算在内 - 只算
js文件的请求,css不算在内 - 如果同时又两个模块满足
cacheGroup的规则要进行拆分,但是maxInitialRequests的值只能允许再拆分一个模块,那尺寸更大的模块会被拆分出来
maxAsyncRequests
maxAsyncRequests和maxInitialRequests有相似之处,它俩都是用来限制拆分数量的,maxInitialRequests是用来限制入口的拆分数量而maxAsyncRequests是用来限制异步模块内部的并行最大请求数的,说白了你可以理解为是每个import()它里面的最大并行请求数量。
这其中要注意以下几点:
import()文件本身算一个请求并不算 js 以外的公共资源请求比如 css
如果同时有两个模块满足
cacheGroup的规则要进行拆分,但是maxInitialRequests的值只能允许再拆分一个模块,那尺寸更大的模块会被拆分出来
其余要点
splitChunks.cacheGroup必须同时满足各个条件才能生效,比如minSize或是minChunks等条件必须同时满足才行splitChunks的配置项都是作用于cacheGroup上的,如果将cacheGroup的默认两个分组vendor和default设置为false,则splitChunks就不会起作用minChunks、maxAsyncRequests、maxInitialRequests的值必须设置为大于等于 1 的数当
chunk没有名字时,通过splitChunks分出的模块的名字用id替代,当然你也可以通过name属性自定义当
父chunk和子chunk同时引入相同的module时,并不会将其分割出来而是删除掉子chunk里面共同的module,保留父chunk的module,这个是因为optimization.removeAvaliableModules默认是true当两个
cacheGroup.priority相同时,先定义的会先命中除了
js,splitChunks也适用于css
Tree Shaking
- 2020.05.19
一个模块里可能有很多个方法,只要其中的某个方法使用到了,则整个文件都会被打包到
bundle中去,tree shaking就是只把用到的方法打入到bundle, 没用到的方法会在ugify阶段被擦除掉,从而减小了包的体积。
使用
webpack默认支持, 在 .barbelrc 里面设置 modules: false 即可。
TIP
webpack4 之后在mode:production 的情况下默认开启。
必须是 ES6 的语法, CJS 的方式不支持,且其中编写的方法不能有副作用,否则就会失效。
副作用解释
对于相同的输入就有相同的输出,不依赖外部环境,也不改变外部环境。
符合上述的描述就可以称为纯函数,反之就是带有副作用。
原理
利用 ES6 模块的特点:
- 只能作为模块顶层的语句出现,只在文件的顶层,不能在代码中动态导入
import的模块名只能是字符串常量import binding是immutable的
代码擦除:
uglify阶段删除无用代码。
扩展
- 2020.05.19
上述描述到如果模块是不纯,那么tree shaking检测就会失效,如何优化这部分的功能呢?
这里可以配合使用另外一个插件webpack-deep-scope-plugin。
webpack-deep-scope-plugin是一位中国同胞(学生)在Google夏令营,在导师 Tobias 带领下写的一个webpack插件。主要用于填充webpack自身Tree-shaking的不足,通过作用域分析来消除无用的代码。
Scope Hoisting
- 2020.05.19
scope hoisting是webpack3的新功能,直译过来就是「作用域提升」。熟悉JavaScript都应该知道「函数提升」和「变量提升」,JavaScript会把函数和变量声明提升到当前作用域的顶部。「作用域提升」也类似于此,webpack会把引入的js文件“提升到”它的引入者顶部。
现象
在未使用Scope Hoisting的情况下,编译后的代码中存在着大量的闭包代码。
// 编译前
// a.js
export default "xxxx";
// b.js
import index from "./a";
console.log(index);
// 编译后
/****/ "./app/index/app.js";
/******************!*\
!*** ./app/index/app.js ***!
\**************************/
/*! no exports provided */
/***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports);
/* harmony import */ var __js_index__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULES_0__ = __webpack_require__(
/*! ./js/index */ "./app/index/app.js"
);
console.log(__js_index__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULES_0__["default"]);
/***/
},
/****/ "./app/index/js/index.js");
/******************!*\
!*** ./app/index/js/index.js ***!
\**************************/
/*! export provided:default */
/***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports);
/* harmony default export */ __webpack_exoirts__["default"] = "xxxx";
/***/
});
这样会导致:
大量闭包函数包裹代码,导致体积增大(模块越多的情况下越明显)
运行代码时创建的函数作用域变多,内存开销变大
原理之模块转化分析
我们来探究下为什么经过webpack打包之后会产生这么多的闭包函数,先来了解下webpack的模块转化。
// 打包之前的代码
import { helloword } from "./helloworld";
import "../../common";
document.write(helloworld());
// 打包之后的模块初始化函数
/* 0 */
/***/(function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__)){
"use strict";
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);
/* harmony import (指es6的import语法)*/ var _common_WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__ = __webpack_require__(1);
/* harmony import */ var _helloworld_WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1__ = __webpack_require__(2);
document.write(Object(_helloworld_WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1__["helloworld"])());
/***/ })
结论
被
webpack转化后的模块会带上一层包裹import会被转化成__webpack_require
进一步分析 webpack 的模块机制
(function(modules){
var installedModules = {};
function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
if (installedModules[moduleId]) {
return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
}
var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
i: moduleId,
l: false,
exports: {}
};
modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
module.l = true;
return module.exports;
}
__webpack_require__(0);
})([
/* 0 module*/
(function (module, __webpack_exports__. __webpack_require__){
...
}),
/* 1 module*/
(function (module, __webpack_exports__. __webpack_require__){
...
}),
/* n module*/
(function (module, __webpack_exports__. __webpack_require__){
...
}),
]);
结论
webpack打包出来的是一个IIFE(匿名闭包)modules是一个数组,每一项是一个模块初始化函数__webpack_require用来加载模块, 返回的是module.exports通过
WEBPACK_REQUIRE_METHOD(0)来启动程序
Scope Hoisting 原理
将所有模块的代码按照引用顺序放在一个函数作用域里, 然后适当的重命名一些变量以防止变量名冲突。

Scope Hoisting 使用
在webpack4下 mode 为 production 时默认开启了此功能。
Code Splitting 和 动态 import
- 2020.05.19
Code Splitting
Code Splitting 一般需要做这些事情:
- 为
Vendor单独打包(Vendor指第三方的库或者公共的基础组件,因为Vendor的变化比较少,单独打包利于缓存)。 - 为
Manifest(Webpack的Runtime代码)单独打包。 - 为不同入口的公共业务代码打包(同理,也是为了缓存和加载速度)。
- 为异步加载的代码打一个公共的包。
Code Splitting 一般是通过配置 CommonsChunkPlugin 来完成的。一个典型的配置如下,分别为 vendor、manifest 和 vendor-async 配置了 CommonsChunkPlugin。
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'vendor',
minChunks (module) {
return (
module.resource &&
/\.js$/.test(module.resource) &&
module.resource.indexOf(
path.join(__dirname, '../node_modules')
) === 0
)
}
}),
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'manifest',
minChunks: Infinity
}),
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'app',
async: 'vendor-async',
children: true,
minChunks: 3
}),
CommonsChunkPlugin 的特点就是配置比较难懂,大家的配置往往是复制过来的,这些代码基本上成了模板代码(boilerplate)。
如果 Code Splitting 的要求简单倒好,如果有比较特殊的要求,比如把不同入口的 vendor 打不同的包,那就很难配置了。总的来说配置 Code Splitting 是一个比较痛苦的事情。
而 Long-term caching 策略是这样的:给静态文件一个很长的缓存过期时间,比如一年。然后在给文件名里加上一个 hash,每次构建时,当文件内容改变时,文件名中的 hash 也会改变。浏览器在根据文件名作为文件的标识,所以当 hash 改变时,浏览器就会重新加载这个文件。
Webpack 的 Output 选项中可以配置文件名的 hash,比如这样:
output: {
path: config.build.assetsRoot,
filename: utils.assetsPath('js/[name].[chunkhash].js'),
chunkFilename: utils.assetsPath('js/[id].[chunkhash].js')
},
如何动态的 import
- 安装 babel 插件
npm install @babel/plugin-syntax-dynamic-import --save-dev
- 配置
.babelrc文件的plugins
{
...,
plugins: [
'@babel/plugin-syntax-dynamic-import',
...
]
}
如何使用
import(path).then((res) => {
// do something
});
内部原理
通过 webpackJsonp 请求异步加载。动态创建script标签,然后引入。
webpack 与 CI/CD 集成
- 2020.05.19
本地开发增加precommit钩子
- 安装
husky
npm install husky --save-dev
- 增加
npm script,通过lint-staged增量检查修改的文件
...,
"scripts": {
"precommit": "lint-staged"
},
"husky": {
"hooks": {
"pre-commit": "git rev-parse --abbrev-ref HEAD | if ! [[ $(xargs) =~ 'gray|master|t\\d*' ]]; then lint-staged; fi",
"commit-msg": "commitlint -E HUSKY_GIT_PARAMS"
}
},
"lint-staged": {
"linters": {
"*.{js,scss}": ["eslint --fix", "git add"]
}
}
webpack 打包组件和基础库
- 2020.05.19
webpack除了打包应用,也可以用来打包 js 库和一些自定义组件库。
TIP
单纯只是打包 js 库和组件库的话 使用rollup打包也是一个不错的选择
我们来实现一个简单的打包例子,这个例子需要满足以下几点功能:
需要支持打包
压缩版(x.min.js)和非压缩版本(x.js)。支持
AMD/CJS/ESM模块引入。支持通过
script脚本直接引入链接。
// ESM
import * as Tool from 'tools';
//cjs
const Tool = require('tools');
// AMD
require(['tools'],function(){
...
})
// script 脚本
<script src="https://xxx.com/tools"></script>
如何将库暴露出去?
library:指定库的全局变量libraryTarget:支持库引入的方式
module.exports = {
mode: 'production',
entry: {
tools: "./src/index.js",
tools.min: "./src/index.js"
},
output:{
filename: "[name].js",
library: "tools",
libraryExport: "default",
libraryTarget: "umd",// var this window ...
}
}
接下来让我们开始表演:
1.新建项目 webpack-build-tools 安装webpack和webpack-cli
mkdir webpack-build-tools
cd webpack-build-tools
npm init -y
npm i webpack webpack-cli
2. 新建目录 src/index.js,编写我们的工具代码
此处的代码来自我的博客下 js-tips 仅作为示例使用
/**
* 将参数中的null undefined转化为空
* @param {String} el
*/
export function transferDefectParams(el) {
return ["null", "undefined"].includes(el) ? "" : el;
}
/**
* 正则表示法
* 思路:通过正则表达式获取url上的参数 然后通过数组reduce追加到对象中
*
* @param {string} url 需要获取的url地址默认为当前地址
*/
export default function getUrlParameters(url = window.location.href) {
/**
* match返回字符串中匹配结果的数组,匹配不到返回null
* [^?=&]+ 匹配除了?=&之外的字符 仅匹配一次
* Array.reduce(callBack(prev,cur,index,array), initialValue)
* Array.slice(start,[end]) 返回start-end的元素
*/
const params = url.match(/([^?=&]+)=([^&]*)/g);
if (params) {
return params.reduce(
(a, v) => (
(a[v.slice(0, v.indexOf("="))] = transferDefectParams(
v.slice(v.indexOf("=") + 1)
)),
a
),
{}
);
}
return {};
}
3. 安装 terser-webpack-plugin 压缩插件
npm i terser-webpack-plugin -D
4. 新建 webpack.config.js
const TerserPlugin = require("terser-webpack-plugin"); // 引入压缩插件
module.exports = {
mode: "none", // 因为默认是production 默认会进行压缩
entry: {
tools: "./src/index.js",
"tools.min": "./src/index.js",
},
output: {
filename: "[name].js",
library: "tools",
libraryExport: "default", // 不添加的话引用的时候需要 tools.default
libraryTarget: "umd", // var this window ...
},
optimization: {
minimize: true,
minimizer: [
new TerserPlugin({
// 使用压缩插件
include: /\.min\.js$/,
}),
],
},
};
5. 修改 package.json 添加打包命令
{
"name": "webpack-build-tools",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "js常用工具函数",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1",
"build": "webpack",
"prepublish": "webpack"
},
"keywords": ["webpack-build-tools"],
"author": "xjl271314",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"webpack": "^4.43.0",
"webpack-cli": "^3.3.11"
},
"devDependencies": {
"terser-webpack-plugin": "^3.0.1"
}
}
6. 打包并查看打包效果
npm run build
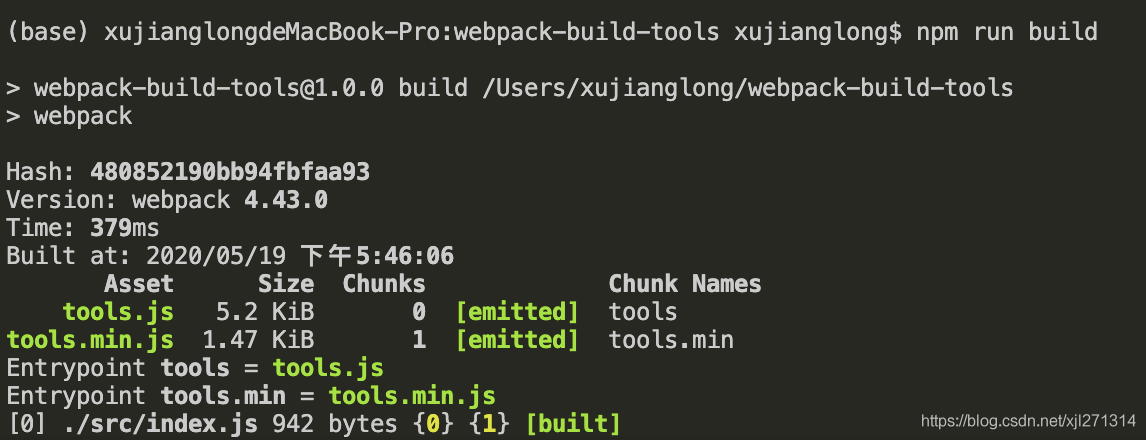
// tools.js
(function webpackUniversalModuleDefinition(root, factory) {
if (typeof exports === "object" && typeof module === "object")
module.exports = factory();
else if (typeof define === "function" && define.amd) define([], factory);
else if (typeof exports === "object") exports["tools"] = factory();
else root["tools"] = factory();
})(window, function() {
return /******/ (function(modules) {
// webpackBootstrap
/******/ // The module cache
/******/ var installedModules = {}; // The require function
/******/
/******/ /******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
/******/
/******/ // Check if module is in cache
/******/ if (installedModules[moduleId]) {
/******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
/******/
} // Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
/******/ /******/ var module = (installedModules[moduleId] = {
/******/ i: moduleId,
/******/ l: false,
/******/ exports: {},
/******/
}); // Execute the module function
/******/
/******/ /******/ modules[moduleId].call(
module.exports,
module,
module.exports,
__webpack_require__
); // Flag the module as loaded
/******/
/******/ /******/ module.l = true; // Return the exports of the module
/******/
/******/ /******/ return module.exports;
/******/
} // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__)
/******/
/******/
/******/ /******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules; // expose the module cache
/******/
/******/ /******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules; // define getter function for harmony exports
/******/
/******/ /******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) {
/******/ if (!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, {
enumerable: true,
get: getter,
});
/******/
}
/******/
}; // define __esModule on exports
/******/
/******/ /******/ __webpack_require__.r = function(exports) {
/******/ if (typeof Symbol !== "undefined" && Symbol.toStringTag) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, Symbol.toStringTag, {
value: "Module",
});
/******/
}
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, "__esModule", { value: true });
/******/
}; // create a fake namespace object // mode & 1: value is a module id, require it // mode & 2: merge all properties of value into the ns // mode & 4: return value when already ns object // mode & 8|1: behave like require
/******/
/******/ /******/ /******/ /******/ /******/ /******/ __webpack_require__.t = function(
value,
mode
) {
/******/ if (mode & 1) value = __webpack_require__(value);
/******/ if (mode & 8) return value;
/******/ if (
mode & 4 &&
typeof value === "object" &&
value &&
value.__esModule
)
return value;
/******/ var ns = Object.create(null);
/******/ __webpack_require__.r(ns);
/******/ Object.defineProperty(ns, "default", {
enumerable: true,
value: value,
});
/******/ if (mode & 2 && typeof value != "string")
for (var key in value)
__webpack_require__.d(
ns,
key,
function(key) {
return value[key];
}.bind(null, key)
);
/******/ return ns;
/******/
}; // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules
/******/
/******/ /******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
/******/ var getter =
module && module.__esModule
? /******/ function getDefault() {
return module["default"];
}
: /******/ function getModuleExports() {
return module;
};
/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, "a", getter);
/******/ return getter;
/******/
}; // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call
/******/
/******/ /******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) {
return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property);
}; // __webpack_public_path__
/******/
/******/ /******/ __webpack_require__.p = ""; // Load entry module and return exports
/******/
/******/
/******/ /******/ return __webpack_require__((__webpack_require__.s = 0));
/******/
})(
/************************************************************************/
/******/ [
/* 0 */
/***/ function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);
/* harmony export (binding) */ __webpack_require__.d(
__webpack_exports__,
"transferDefectParams",
function() {
return transferDefectParams;
}
);
/* harmony export (binding) */ __webpack_require__.d(
__webpack_exports__,
"default",
function() {
return getUrlParameters;
}
);
/**
* 将参数中的null undefined转化为空
* @param {String} el
*/
function transferDefectParams(el) {
return ["null", "undefined"].includes(el) ? "" : el;
}
/**
* 正则表示法
* 思路:通过正则表达式获取url上的参数 然后通过数组reduce追加到对象中
*
* @param {string} url 需要获取的url地址默认为当前地址
*/
function getUrlParameters(url = window.location.href) {
/**
* match返回字符串中匹配结果的数组,匹配不到返回null
* [^?=&]+ 匹配除了?=&之外的字符 仅匹配一次
* Array.reduce(callBack(prev,cur,index,array), initialValue)
* Array.slice(start,[end]) 返回start-end的元素
*/
const params = url.match(/([^?=&]+)=([^&]*)/g);
if (params) {
return params.reduce(
(a, v) => (
(a[v.slice(0, v.indexOf("="))] = transferDefectParams(
v.slice(v.indexOf("=") + 1)
)),
a
),
{}
);
}
return {};
}
/***/
},
/******/
]
)["default"];
});
// tools.min.js
!(function(e, t) {
"object" == typeof exports && "object" == typeof module
? (module.exports = t())
: "function" == typeof define && define.amd
? define([], t)
: "object" == typeof exports
? (exports.tools = t())
: (e.tools = t());
})(window, function() {
return (function(e) {
var t = {};
function n(r) {
if (t[r]) return t[r].exports;
var o = (t[r] = { i: r, l: !1, exports: {} });
return e[r].call(o.exports, o, o.exports, n), (o.l = !0), o.exports;
}
return (
(n.m = e),
(n.c = t),
(n.d = function(e, t, r) {
n.o(e, t) || Object.defineProperty(e, t, { enumerable: !0, get: r });
}),
(n.r = function(e) {
"undefined" != typeof Symbol &&
Symbol.toStringTag &&
Object.defineProperty(e, Symbol.toStringTag, { value: "Module" }),
Object.defineProperty(e, "__esModule", { value: !0 });
}),
(n.t = function(e, t) {
if ((1 & t && (e = n(e)), 8 & t)) return e;
if (4 & t && "object" == typeof e && e && e.__esModule) return e;
var r = Object.create(null);
if (
(n.r(r),
Object.defineProperty(r, "default", { enumerable: !0, value: e }),
2 & t && "string" != typeof e)
)
for (var o in e)
n.d(
r,
o,
function(t) {
return e[t];
}.bind(null, o)
);
return r;
}),
(n.n = function(e) {
var t =
e && e.__esModule
? function() {
return e.default;
}
: function() {
return e;
};
return n.d(t, "a", t), t;
}),
(n.o = function(e, t) {
return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e, t);
}),
(n.p = ""),
n((n.s = 0))
);
})([
function(e, t, n) {
"use strict";
function r(e) {
return ["null", "undefined"].includes(e) ? "" : e;
}
function o(e = window.location.href) {
const t = e.match(/([^?=&]+)=([^&]*)/g);
return t
? t.reduce(
(e, t) => (
(e[t.slice(0, t.indexOf("="))] = r(
t.slice(t.indexOf("=") + 1)
)),
e
),
{}
)
: {};
}
n.r(t),
n.d(t, "transferDefectParams", function() {
return r;
}),
n.d(t, "default", function() {
return o;
});
},
]).default;
});
7.设置入口文件 不同环境下使用不同的入口文件
package.json中的main字段为index.js,所以在项目根目录下新建 index.js
// index.js
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === "production") {
// 通过环境变量来决定入口文件
module.exports = require("./dist/tools.min.js");
} else {
module.exports = require("./dist/tools.js");
}
8.进行 npm 包发布(需要注册 npm 账号,且进行登录)
npm publish
9. 同步代码到 git,并编写对应的说明文档等
// 其他项目引用
npm i tools -s
import getUrlParameters from 'tools';
TIP
完整代码参见github 地址
webpack 实现 SSR 打包
- 2020.05.19
客户端渲染: HTML + CSS + JS + Data ————> 渲染后的 HTML
服务端渲染:
所有的模板等资源都存储在服务器
内网机器拉取更快
一个 HTML 返回所有的数据
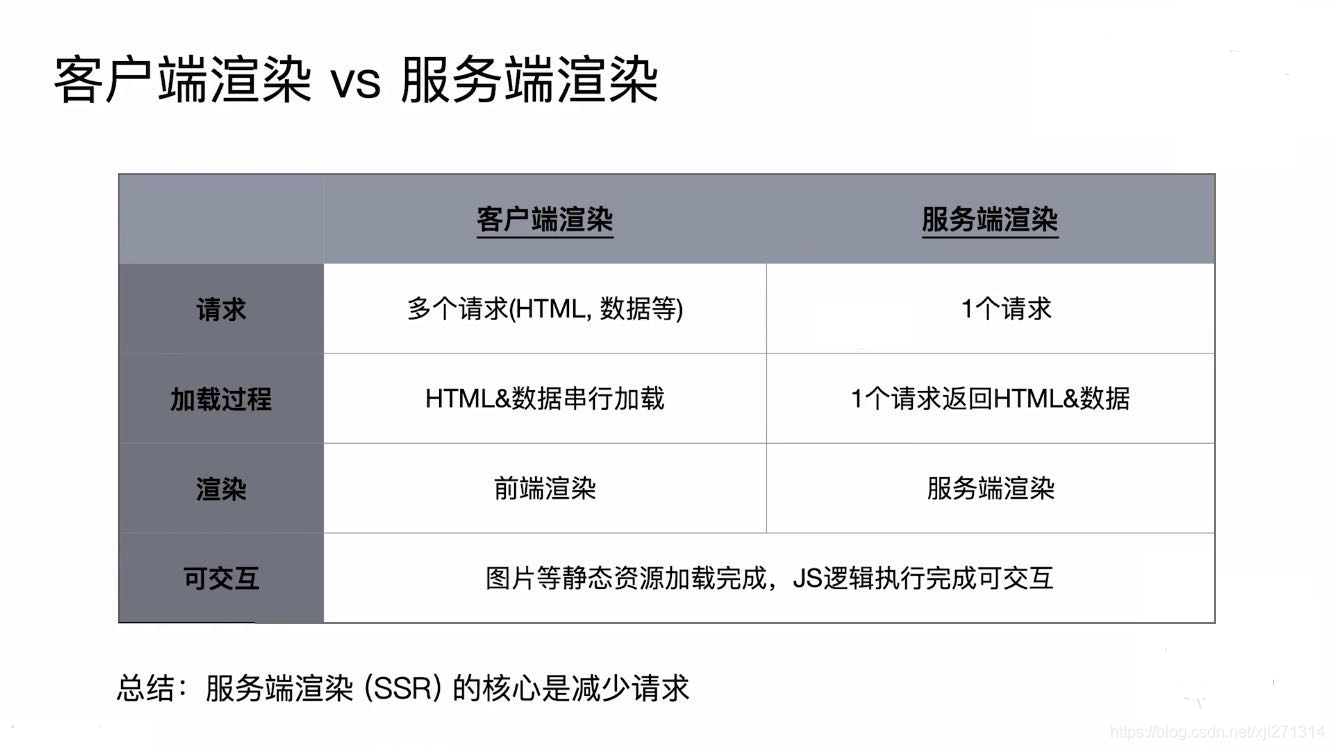
SSR 代码实现思路
- 服务端:
使用
react-dom/server的renderToString方法将React组件渲染成字符串。服务端路由返回对应的模板。
- 客户端
打包出针对服务端的组件。
简单示例
// package.json
"script":{
...,
"build:ssr": "webpack --config webpack.ssr.js"
}
目录下新建 server/index.js
/* server/index.js */
// 兼容window报错
if (typeof window === "undefined") {
global.window = {};
}
const express = require("express");
const { renderToString } = require("react-dom/server");
const SSR = require("../dist/xx-server");
const server = (port) => {
const app = express();
app.use(express.static("dist"));
app.get("/search", (req, res) => {
const html = renderMarkup(renderToString(SSR));
res.status(200).send(html);
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log("Server is running on port:", port);
});
};
server(process.env.PORT || 3000);
const renderMarkup = (str) => {
return `<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">${str}</div>
</body>
</html>`;
};
组件目录下创建index-server.js
// index-server.js server端不能识别import 需要使用commonjs规范
"use strict";
const React = require("react");
const Example = () => <div>Hello World</div>;
module.exports = <Example />;
创建 webpack.ssr.js
// webpack.ssr.js
module.exports = {
...,
output:{
path: path.join(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: '[name-server].js',
libraryTarget: 'umd'
}
}
打包过程中遇到的问题
浏览器的全局变量(Node.js 中没有document, window)
组件适配: 将不兼容的组件根据打包环境进行适配
请求适配: 将
fetch或者ajax发送请求的写法改成isomorphic-fetch或者axios
样式问题(Node.js 无法解析CSS)
服务端打包通过
ignore-loader忽略掉CSS的解析将
style-loader替换成isomorphic-style-loader或者使用内联样式
style
解决打包样式问题
使用打包出来的浏览器端 html 文件作为模板, 设置占位符, 动态插入组件。
修改 /server/index.js
const template = fs.readFileSync("xxx");
修改对应的 template.html
<div id="root"><!-- HTML_PLCAEHOLDER ---></div>
优化构建时命令行的显示
- 2020.05.26
实际开发过程中当我们进行打包npm run build或者在开发过程中npm run dev的时候会在控制台输出大量的信息。
使用 friendly-errors-webpack-plugin 优化日志显示
success: 构建成功的日志提示warning: 构建警告的日志提示error: 构建报错的日志提示
stats: 'errors-only'
...
plugins:[
...,
new FriendlyErrorsWebpackPlugin()
]
CommonsChunkPlugin
- 2020.05.18
主要是用来提取第三方库和公共模块,避免
首屏加载的bundle文件或者按需加载的bundle文件体积过大,从而导致加载时间过长,是一把优化项目的利器。
TIP
webpack4之后推荐使用splitChunks替代该方法。
chunk 有哪几种,主要有以下三种:
webpack当中配置的入口文件(entry)是chunk,可以理解为entry chunk入口文件以及它的依赖文件通过
code split(代码分割)出来的也是chunk,可以理解为children chunk通过
commonsChunkPlugin创建出来的文件也是chunk,可以理解为commons chunk
可配置的属性:
| 属性名 | 属性说明 |
|---|---|
name | 可以是已经存在的chunk(一般指入口文件)对应的name,那么就会把公共模块代码合并到这个chunk上;否则,就会创建名字为name的commons chunk进行合并 |
filename | 指定commons chunk的文件名 |
chunks | 指定该source chunk,即指定从哪些chunk当中去找公共模块,省略该选项的时候,默认就是entry chunks |
minChunks | 既可以数字,也可以是函数,还可以是Infinity |
插件的作用:
单独分离出第三方库、自定义公共模块、webpack 运行文件
- 抽离 webpack 运行文件,修改 webpack 配置文件:
plugins: [
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: ["vendor", "runtime"],
filename: "[name].js",
minChunks: Infinity,
}),
];
上面这段抽离webpack运行文件代码的意思是创建一个名为runtime的commons chunk进行webpack运行文件的抽离,其中source chunks是vendor.js。
CleanWebpackPlugin
清理构建目录
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin();
]
ExtractTextWebpackPlugin
将 CSS 从 bundle 中提取成一个独立的 css 文件
CopyWebpackPlugin
将文件或者文件夹拷贝到构建的输出目录
UglifyjsWebpackPlugin
压缩 JS
ZipWebpackPlugin
将打包出的资源生成一个 zip 包
MiniCssExtractPlugin
- 2020.05.29
将 css 打包成单独的 css 文件
// npm i mini-css-extract-plugin
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require("mini-css-extract-plugin");
const path = require("path");
module.exports = {
mode: "development", //打包为开发模式
entry: "./src/main", //入口文件,从项目根目录指定
output: {
//输出路径和文件名,使用path模块resolve方法将输出路径解析为绝对路径
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "../dist/js"), //将js文件打包到dist/js的目录
filename: "main.js",
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader,
{
loader: "css-loader",
options: {
minimize: true,
},
},
],
},
],
},
plugins: [
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
filename: "../css/styles.css", //如果需要将css文件单独放入css文件夹中需要../
}),
],
};
HtmlWebpackPlugin
HtmlWebpackPluginstar: 8.5K主要有两个作用:
为
html文件中引入的外部资源如script、link动态添加每次compile后的hash,防止引用缓存的外部文件问题可以生成创建
html入口文件,比如单页面可以生成一个html文件入口,配置 N 个html-webpack-plugin可以生成 N 个页面入口
常用的字段:
title:设置生成html文件的标题 默认值为:Webpack Appfilename: 输出的html的文件名称 默认值为:index.htmltemplate: html 模板所在的文件路径
根据自己的指定的模板文件来生成特定的
html文件。这里的模板类型可以是任意你喜欢的模板,可以是html,jade,ejs,hbs, 等等,但是要注意的是,使用自定义的模板文件时,需要提前安装对应的loader, 否则webpack不能正确解析。inject:注入选项。true:默认值,script 标签位于 html 文件的 body 底部body:script 标签位于 html 文件的 body 底部(同 true)head:script 标签位于 head 标签内false:不插入生成的 js 文件,只是单纯的生成一个 html 文件
favicon:给生成的html文件生成一个favicon。属性值为favicon文件所在的路径名minify:对html文件进行压缩,minify的属性值是一个压缩选项或者false。默认值为false, 不对生成的html文件进行压缩。plugins: [ new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ // 部分省略,具体看minify的配置 minify: { //是否对大小写敏感,默认false caseSensitive: true, //是否简写boolean格式的属性如:disabled="disabled" 简写为disabled 默认false collapseBooleanAttributes: true, //是否去除空格,默认false collapseWhitespace: true, //是否压缩html里的css(使用clean-css进行的压缩) 默认值false; minifyCSS: true, //是否压缩html里的js(使用uglify-js进行的压缩) minifyJS: true, //Prevents the escaping of the values of attributes preventAttributesEscaping: true, //是否移除属性的引号 默认false removeAttributeQuotes: true, //是否移除注释 默认false removeComments: true, //从脚本和样式删除的注释 默认false removeCommentsFromCDATA: true, //是否删除空属性,默认false removeEmptyAttributes: true, //若开启此项,生成的html中没有 body 和 head,html也未闭合 removeOptionalTags: false, //删除多余的属性 removeRedundantAttributes: true, //删除script的类型属性,在h5下面script的type默认值:text/javascript 默认值false removeScriptTypeAttributes: true, //删除style的类型属性, type="text/css" 同上 removeStyleLinkTypeAttributes: true, //使用短的文档类型,默认false useShortDoctype: true, }, }), ];hash:给生成的js文件一个独特的hash值,该hash值是该次webpack编译的hash值。默认值为false。
plugins: [ new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ hash: true }) ] // 编译后 <script type=text/javascript src=bundle.js?22b9692e22e7be37b57e></script>cache:默认是true的,表示内容变化的时候生成一个新的文件。showErrors:如果 webpack 编译出现错误,webpack 会将错误信息包裹在一个 pre 标签内,属性的默认值为 true ,也就是显示错误信息。开启这个,方便定位错误.chunks:chunks 主要用于多入口文件,当你有多个入口文件,那就会编译后生成多个打包后的文件,那么chunks就能选择你要使用那些 js 文件。
entry: { index: path.resolve(__dirname, './src/index.js'), devor: path.resolve(__dirname, './src/devor.js'), main: path.resolve(__dirname, './src/main.js') }, plugins: [ new httpWebpackPlugin({ chunks: ['index','main'] }) ] // 打包后 <script type=text/javascript src="index.js"></script> <script type=text/javascript src="main.js"></script> // 而如果没有指定 chunks 选项,默认会全部引用。excludeChunks:排除掉一些 js 不进行打包
path 与 publicPath
在复杂的项目里可能会有一些构建出的资源需要异步加载,加载这些异步资源需要对应的 URL 地址。
output.publicPath配置发布到线上资源的 URL 前缀,为string类型,默认值是字符串’’,即使用相对路径。
例如:需要将构建出的资源文件上传到 CDN 服务上,以利于加快页面的打开速度,配置代码如下:
filename: "[name]_[chunkhash:8].js";
publicPath: "https://cdn.example.com/assets/";
path是webpack构建后输出构建结果的目录,必须是绝对路径.publicPath并不会对生成文件的路径造成影响,主要是对你的页面里面引入的资源的路径做对应的补全,常见的就是 css 文件里面引入的图片 url 值.
构建配置抽离成 npm 包
- 2020.05.26
意义
通用性
- 业务的开发者无需关注构建配置
- 统一团队构建脚本
可维护性
- 构建配置合理的拆分
- README 文档、ChangeLog 文档等
质量
- 冒烟测试
- 持续集成
可选方案
1. 通过配置多个文件区分不同环境的构建 webpack --config 进行参数的控制
- 基础环境: webpack.base.js
- 开发环境: webpack.dev.js
- 生成环境: webpack.prod.js
- SSR 环境: webpack.ssr.js
- PWA 环境: webpack.pwa.js
2. 将构建配置设计成一个库, 比如 hjs-webpack
- 规范: Git Commit 日志、README 文档、ESlint 规范、Semver 规范等
- 质量: 冒烟测试、单元测试、测试覆盖率和 CI 等
3. 抽离成一个工具进行管理, 比如 create-react-app
4. 将所有配置放在一个文件,通过一个 --env 参数控制分支选择
组合
推荐使用
webpack-merge组合我们的配置
const merge = require("webpack-merge");
module.exports = merge(baseConfig, devConfig);
构建包功能模块设计
- 2020.05.27
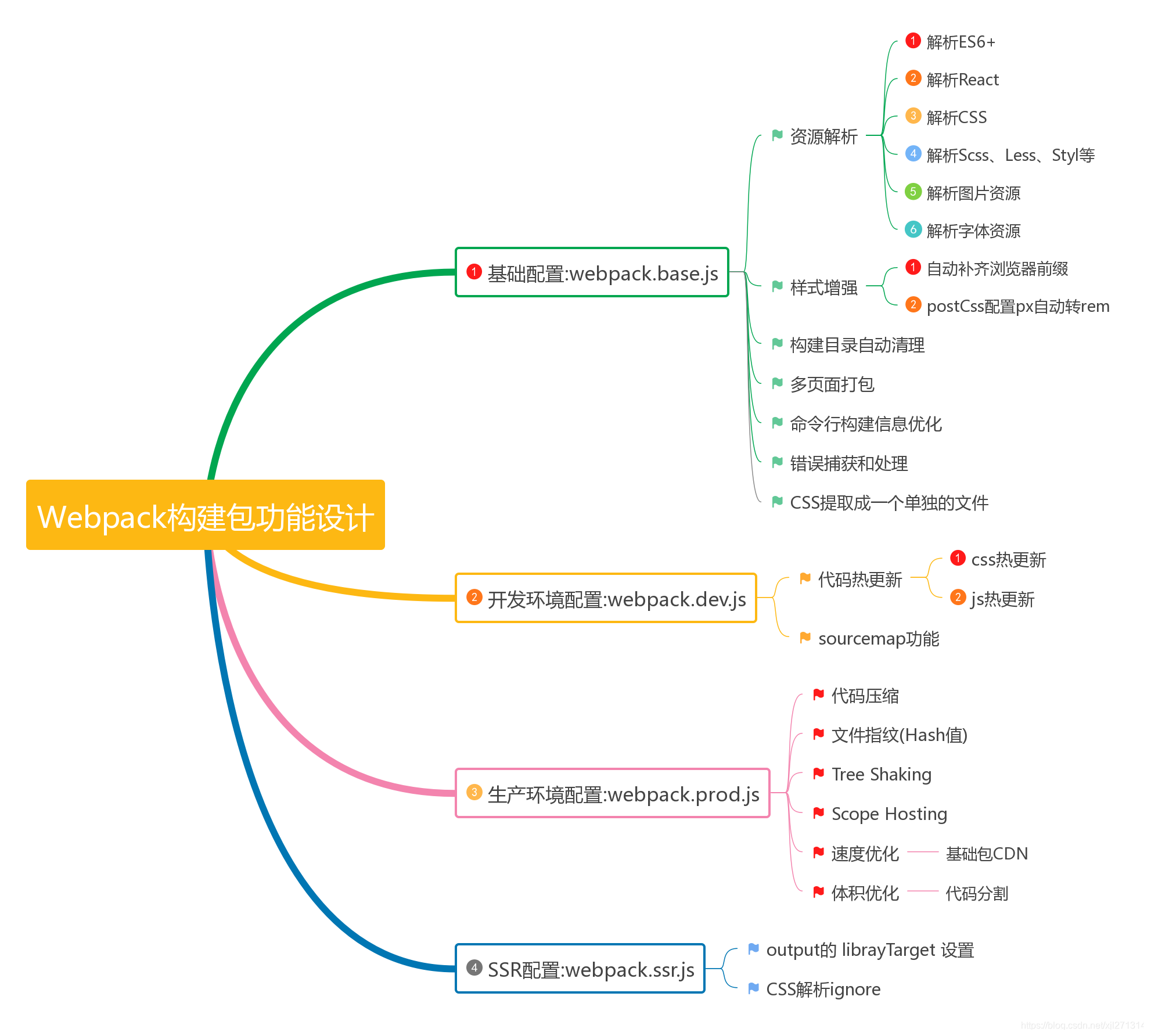
目录结构设计
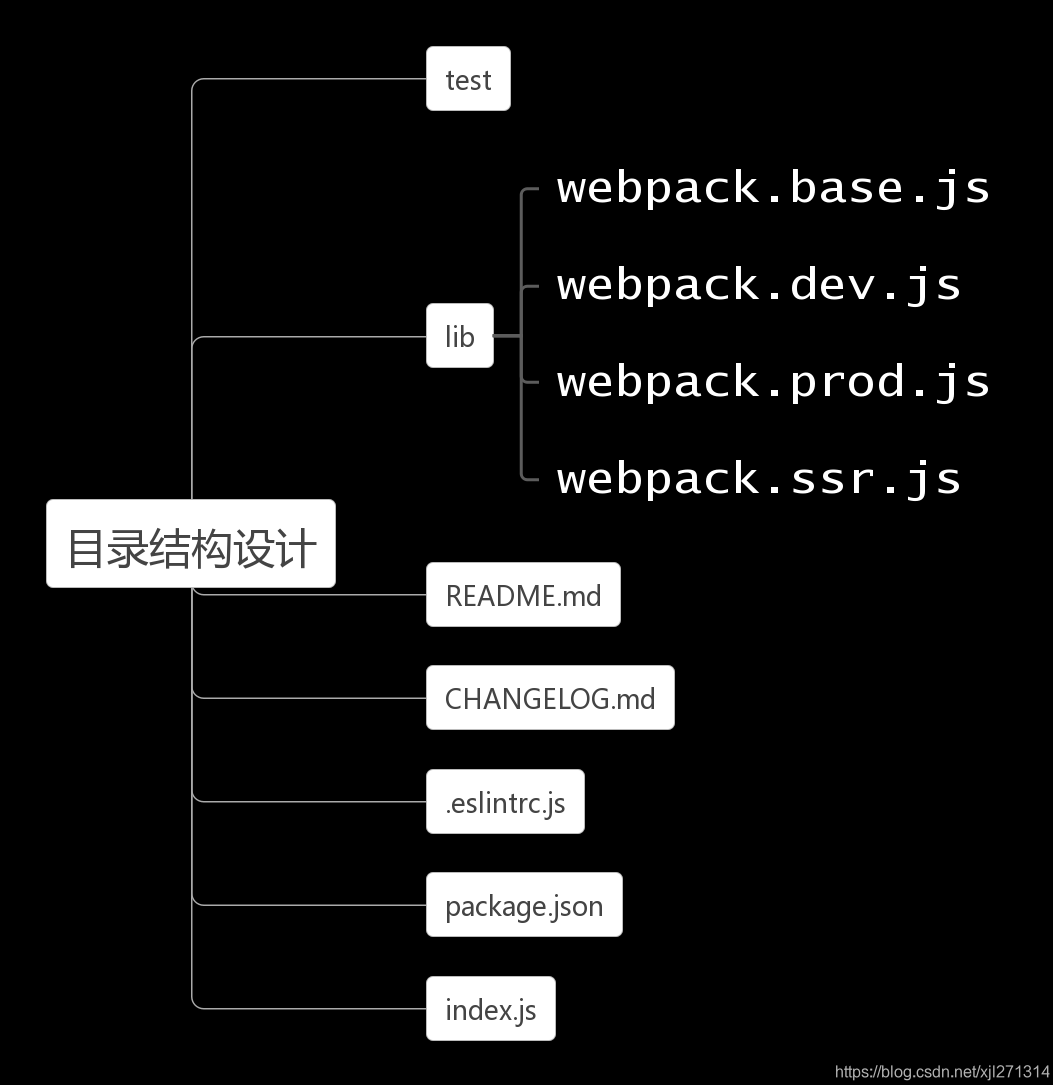
冒烟测试
- 2020.6.01
判断构建是否成功
判断基本功能是否正常
借助第三方工具 jest 等。
单元测试和测试覆盖率
- 2020.06.01
单纯的测试框架,需要断言库
- chai
- mocha
- ava
- should.js
- expect
- better-assert
集成框架,开箱即用
- jest
- jasmine
编写单元测试用例

单元测试的接入
- 安装相关的插件
npm i mocha chai -D
新建
test目录, 并增加xxx.test.js测试文件在
package.json中的scripts字段增加test命令
"scripts": {
...,
"test": "node_modules/mocha/bin/_mocha"
}
- 执行测试命令
npm run test
验证测试覆盖率
npm i -g istanbul
修改 script
"scripts": {
...,
"test": "istanbul cover node_modules/mocha/bin/_mocha"
}
构建包的持续集成和 Travis CI
- 2020.07.27
接入 Travis CI
https://travis-ci.org 使用 Github 账号登录
在https://travis-ci.org/account/repositories为项目开启
项目根目录下新增 .travis.yml
具体流程可以参考官方文档
发布构建包到 npm
- 2020.07.27
添加用户
npm adduser
升级版本
升级补丁版本号: npm version patch
升级小版本号: npm version minor
升级大版本号: npm version major
发布版本
npm publish
TIP
发布的时候需要去搜索下 当前包名是否已经被使用。包里不要带上一些不相干的文件。
使用 webpack 内部的 stats 进行构建包的初步分析
- 2020.07.28
webpack 内部给我们提供了一个 stats 的功能,我们可以在 script 中配置。
// package.json
"scripts":{
"build:stats": "webpack --env production --json > stats.json"
}
...
在 Node.js 中使用
const webpack = require("webpack");
const config = require("./webpack.config.js")("production");
webpack(config, (err, stats) => {
if (err) {
return console.error(err);
}
if (stats.hasErrors()) {
return console.error(stats.toString("errors-only"));
}
console.log(stats);
});
这种方式可以达到简单的分析效果 但是颗粒度太细,看不太出问题的所在。
使用 speed-measure-webpack-plugin 进行速度分析
- 2020.07.28
使用该插件可以直观的看到每个 loader 和插件执行耗时以及打包的总耗时。
const SpeedMeasureWebpackPlugin = require('speed-measure-webpack-plugin');
const smp = new SpeedMeasureWebpackPlugin();
const webpackVonfig = smp.wrap({
plugins:[
// 需要分析的插件
new MyPlugin();
new MyOtherPlugin();
]
})
TIP
构建比较耗时的会显示为红色,构建较耗时的会显示为黄色,构建速度正常的会显示为绿色。
使用 webpack-bundle-analyzer 进行体积分析
- 2020.07.29
使用该插件可以分析项目内依赖的第三方模块文件的大小以及业务内组件代码的大小。
const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin;
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new BundleAnalyzerPlugin();
]
}
构建完成后会在 8888 端口进行构建包大小的展示。
多进程/多实例并行压缩
- 2020.08.07
使用 parallel-uglify-plugin
const parallelUglifyPlugin = require("parallel-uglify-plugin");
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new parallelUglifyPlugin({
uglifyJS: {
output: {
beautify: false,
comments: false,
},
compress: {
warning: false,
drop_console: true,
collapse_vars: true,
reduce_vars: true,
},
},
}),
],
};
使用 uglifyjs-webpack-plugin 并开启 parallel 参数
const UglifyJsPlugin = require("uglifyjs-webpack-plugin");
module.exports = {
plugin: [
new UglifyJsPlugin({
uglifyOptions: {
warnings: false,
parse: {},
compress: {},
mangle: true,
output: null,
toplevel: false,
nameCache: null,
ie8: false,
keep_names: false,
},
parallel: true,
}),
],
};
使用 terser-webpack-plugin 开启 parallel 参数
const TerserPlugin = require("terser-webpack-plugin");
module.exports = {
optimization: {
minimizer: [
new TerserPlugin({
parallel: 4,
}),
],
},
};
通过设置 Externals 进行分包
- 2020.08.07
使用 html-webpack-externals-plugin
const HtmlWebpackExternalsPlugin = require("html-webpack-externals-plugin");
module.exports = {
plugin: [
new HtmlWebpackExternalsPlugin({
externals: [
{
module: "react",
entry: "react_cdn_url",
global: "React",
},
{
module: "react-dom",
entry: "react_dom_url",
global: "ReactDom",
},
],
}),
],
};
进一步分包:采用预编译资源模块
思路: 将 react、react-dom、redux、react-redux 基础包和业务基础包打包成一个文件。
方法: 使用 DLLPlugin进行分包,DllReferencePlugin 对 manifest.json 引用。
const path = require("path");
const webpack = require("webpack");
module.exports = {
context: process.cwd(),
resolve: {
extensions: [".js", ".jsx", ".json", ".less", ".css", ".scss"],
modules: [__driname, "node_modules"],
},
entry: {
library: ["react", "react-dom", "redux", "react-redux"],
},
output: {
filename: "[name].dll.js",
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "./build/library"),
library: "[name]",
},
plugins: [
new webpack.DLLPlugin({
name: "[name]",
path: "./build/library/[name].json",
}),
],
};
包构建完成后,在webpack.config.js中引入
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new webpack.DllReferencePlugin({
manifest: require("./build/library/manifest.json"),
}),
],
};
引用效果,会在 html 文件中加入一个脚本。
<script src="/build/library/library.dll.js"></script>
完整的配置示例:
// webpack.dll.js
const path = require("path");
const webpack = require("webpack");
module.exports = {
entry: {
library: ["react", "react-dom", "redux", "react-redux"],
},
output: {
filename: "[name]_[chunkhash].dll.js",
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "./build/library"),
library: "[name]", // 暴露库的名字
},
plugins: [
new webpack.DLLPlugin({
name: "[name]_[hash]",
path: path.join(__dirname, "build/library/[name].json"),
}),
],
};
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new webpack.DllReferencePlugin({
manifest: require("./build/library/manifest.json"),
}),
],
};
充分利用缓存提升二次构建速度
缓存思路:
babel-loder开启缓存terser-webpack-plugin开启缓存- 使用
cache-loader或者hard-source-webpack-plugin
// babel-loder 开启缓存
loaders: ['babel-loader?cacheDirectory=true']
// terser-webpack-plugin 开启缓存
optimization: {
minizer: [
new TerserPlugin({
parallel: true,
cache: true
})
]
}
// hard-source-webpack-plugin(https://github.com/mzgoddard/hard-source-webpack-plugin)
var HardSourceWebpackPlugin = require('hard-source-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
context: // ...
entry: // ...
output: // ...
plugins: [
new HardSourceWebpackPlugin()
]
}
缩小构建目标
- 2020.08.13
尽可能的少构建模块。
比如 babel-loader 不解析 node_modules
module.exports = {
rules: {
test: "/.js$",
loader: "happypack/loader",
exclude: "node_modules",
},
};
减少文件搜索范围
- 优化
resolve.modules配置(减少模块搜索层级) - 优化
resolve.mainFields配置 - 优化
resolve.extensions配置 - 合理使用
alias
module.exports = {
resolve: {
alias: {
react: path.resolve(__dirname, "./node_modules/react/dist/react.min.js"),
},
modules: [path.resolve(__dirname, "node_modules")], // 先找项目内 找不到直接去node_modules找 以减少模块搜索的层级
extensions: [".js"], // import一个文件没有后缀 优先查找.js文件 如果数组内配置较多 查找也比较耗时
mainFields: ["main"],
},
};
Tree Shaking 在 CSS 中的优化
- 2020.08.13
之前的章节中已经介绍过Tree Shaking 的相关原理和在 js 中的使用,那么如何在CSS中也进行相应的优化呢?
PurifyCSS: 遍历代码,识别已经用到的 CSS Class。uncss:HTML需要通过jsdom加载,所有的样式通过PostCss解析,通过document.querySelector来识别在html文件里面不存在的选择器。
这里将使用 purgecss-webpack-plugin 配合 mini-css-extract-plugin 来使用。
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require("mini-css-extract-plugin");
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
// Options similar to the same options in webpackOptions.output
// both options are optional
filename: "[name].css",
chunkFilename: "[id].css",
}),
],
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
{
loader: MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader,
options: {
publicPath: "/public/path/to/",
},
},
"css-loader",
],
},
],
},
};
// PurgecssPlugin
const PurgecssPlugin = require("purgecss-webpack-plugin");
const PATHS = {
src: path.join(__dirname, "src"),
};
new PurgecssPlugin({
paths: glob.sync(`${PATHS.src}/**/*`, { nodir: true }),
});
使用 webpack 进行图片压缩
- 2020.08.13
要求: 基于 Node库的 imagemin 或者 tinypng API
使用: 配置 image-webpack-plugin
使用 Imagemin 的优点分析
有很多定制选项
可以引入更多第三方优化插件,例如 pngquant
可以处理多种图片格式
return {
test: "/.(png|svg|jpg|gif|blob)",
use: [
{
loader: "file-loader",
options: {
name: `${filename}img/[name]${hash}.[ext]`,
},
},
{
loader: "image-webpack-loader",
options: {
mozjpeg: {
progressive: true,
quality: 65,
},
optipng: {
enabled: false,
},
pngquant: {
quality: "65-90",
speed: 4,
},
gifsicle: {
interlaced: false,
},
webp: {
quality: 75,
},
},
},
],
};
Imagemin 的压缩原理
pngquant: 一款 PNG 压缩器,通过将图像转化为具有alpha通道(通常比 24/32 位 PNG 文件小 60-80%)的更高效的 8 位 PNG 格式,可显著减小文件大小。pngcrush: 其主要目的是通过尝试不同的压缩级别和 PNG 过滤方法来降低 PNG IDAT 数据流的大小。optipng: 其设计灵感来自于pngcrush。optipng可将图像文件重新压缩为更小尺寸,而不会失去任何信息。tinypng: 将 24 位 png 文件转化为更小有索引的 8 位图片,同时所有非必要的metadata也会被剥离掉。
使用动态的 Ployfill 优化构建体积
- 2020.08.14
| 方案 | 优点 | 缺点 | 建议 |
|---|---|---|---|
babel-polyfill | React16 官方推荐方案 | 1. 包体积约 200K+,难以单独抽离 Map、Set。 2. 项目里 react 是单独引用的 cdn,如果用使用的话,需要单独构建一份放在 react 前加载。 | 不建议采用 |
babel-plugin-transform-runtime | 能只 polyfill 用到的类或方法,相对体积较小 | 不能 polyfill 原型上的方法,不适用于业务项目的复杂开发环境 | 不建议采用 |
自己写Map、Set的polyfill | 定制化高,体积小 | 1. 重复造轮子,容易在日后年久失修或者成为坑 2. 即使体积小,依然所以用户都要加载。 | 不建议采用 |
polyfill-service | 只给用户返回需要的 polyfill,社区维护 | 部分国内奇葩浏览器 UA 可能无法识别(但是可以降级返回所需全部 polyfill) | 推荐使用 |
Polyfill Service 原理
识别访问的
User Agent,下发不同的Polyfill
<script src="https://cdn.polyfill.io/v2/polyfill.min.js"></script>
webpack 启动过程分析
- 2020.08.14
思考:
通过
npm scripts运行webpack-开发环境:npm run dev-生产环境:npm run build通过 webpack 直接运行
webpack entry.js bundle.js
这个过程到底发生了什么???
1. 查找 webpack 入口文件
在命令行运行以上命令后,
npm会让命令行工具进入node_modules/.bin目录查找是否存在webpack.sh(mac)或者webpack.cmd(windows)文件,如果存在就执行,不存在就抛出错误。
实际的入口文件是: node_modules/webpack/bin/webpack.js 找到之后执行其中的代码。
2. 分析 webpack 的入口文件 webpack.js 到底做了什么事情
#!/usr/bin/env node
// @ts-ignore 正常执行的返回值
process.exitCode = 0;
/**
* 运行某个命令之后返回一个promise
* @param {string} command process to run
* @param {string[]} args commandline arguments
* @returns {Promise<void>} promise
*/
const runCommand = (command, args) => {
const cp = require("child_process");
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const executedCommand = cp.spawn(command, args, {
stdio: "inherit",
shell: true,
});
executedCommand.on("error", (error) => {
reject(error);
});
executedCommand.on("exit", (code) => {
if (code === 0) {
resolve();
} else {
reject();
}
});
});
};
/**
* 判断某个包是否安装
* @param {string} packageName name of the package
* @returns {boolean} is the package installed?
*/
const isInstalled = (packageName) => {
try {
require.resolve(packageName);
return true;
} catch (err) {
return false;
}
};
/**
* webpack可用的CLI:webpack-cli 和 webpack-command
* @typedef {Object} CliOption
* @property {string} name display name
* @property {string} package npm package name
* @property {string} binName name of the executable file
* @property {string} alias shortcut for choice
* @property {boolean} installed currently installed?
* @property {boolean} recommended is recommended
* @property {string} url homepage
* @property {string} description description
*/
/** @type {CliOption[]} */
const CLIs = [
{
name: "webpack-cli",
package: "webpack-cli",
binName: "webpack-cli",
alias: "cli",
installed: isInstalled("webpack-cli"),
recommended: true,
url: "https://github.com/webpack/webpack-cli",
description: "The original webpack full-featured CLI.",
},
{
name: "webpack-command",
package: "webpack-command",
binName: "webpack-command",
alias: "command",
installed: isInstalled("webpack-command"),
recommended: false,
url: "https://github.com/webpack-contrib/webpack-command",
description: "A lightweight, opinionated webpack CLI.",
},
];
// 判断两个CLI是否安装了
const installedClis = CLIs.filter((cli) => cli.installed);
// 根据安装的CLI数量进行处理
if (installedClis.length === 0) {
const path = require("path");
const fs = require("fs");
const readLine = require("readline");
let notify =
"One CLI for webpack must be installed. These are recommended choices, delivered as separate packages:";
for (const item of CLIs) {
if (item.recommended) {
notify += `\n - ${item.name} (${item.url})\n ${item.description}`;
}
}
console.error(notify);
const isYarn = fs.existsSync(path.resolve(process.cwd(), "yarn.lock"));
const packageManager = isYarn ? "yarn" : "npm";
const installOptions = [isYarn ? "add" : "install", "-D"];
console.error(
`We will use "${packageManager}" to install the CLI via "${packageManager} ${installOptions.join(
" "
)}".`
);
const question = `Do you want to install 'webpack-cli' (yes/no): `;
const questionInterface = readLine.createInterface({
input: process.stdin,
output: process.stderr,
});
questionInterface.question(question, (answer) => {
questionInterface.close();
const normalizedAnswer = answer.toLowerCase().startsWith("y");
if (!normalizedAnswer) {
console.error(
"You need to install 'webpack-cli' to use webpack via CLI.\n" +
"You can also install the CLI manually."
);
process.exitCode = 1;
return;
}
const packageName = "webpack-cli";
console.log(
`Installing '${packageName}' (running '${packageManager} ${installOptions.join(
" "
)} ${packageName}')...`
);
runCommand(packageManager, installOptions.concat(packageName))
.then(() => {
require(packageName); //eslint-disable-line
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
});
} else if (installedClis.length === 1) {
const path = require("path");
const pkgPath = require.resolve(`${installedClis[0].package}/package.json`);
// eslint-disable-next-line node/no-missing-require
const pkg = require(pkgPath);
// eslint-disable-next-line node/no-missing-require
require(path.resolve(
path.dirname(pkgPath),
pkg.bin[installedClis[0].binName]
));
} else {
console.warn(
`You have installed ${installedClis
.map((item) => item.name)
.join(
" and "
)} together. To work with the "webpack" command you need only one CLI package, please remove one of them or use them directly via their binary.`
);
// @ts-ignore
process.exitCode = 1;
}
TIP
webpack 启动后的结果:
webpack最终找到 webpack-cli(webpack-command)这个npm包,并且执行CLI命令。
webpack-cli 源码阅读
- 2020.08.14
webpack-cli 做的事情
引入了
yargs,对命令进行定制分析命令行参数,对各个参数进行转换,组成编译配置项
引用
webpack,根据配置项进行编译和构建
1.从 NON_COMPILATION_CDM 分析出不需要编译的命令
webpack-cli处理不需要经过编译的命令
#!/usr/bin/env node
/*
MIT License http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php
Author Tobias Koppers @sokra
*/
const { NON_COMPILATION_ARGS } = require("./utils/constants");
(function() {
// wrap in IIFE to be able to use return
const importLocal = require("import-local");
// Prefer the local installation of webpack-cli
if (importLocal(__filename)) {
return;
}
require("v8-compile-cache");
const ErrorHelpers = require("./utils/errorHelpers");
const NON_COMPILATION_CMD = process.argv.find((arg) => {
if (arg === "serve") {
global.process.argv = global.process.argv.filter((a) => a !== "serve");
process.argv = global.process.argv;
}
return NON_COMPILATION_ARGS.find((a) => a === arg);
});
if (NON_COMPILATION_CMD) {
return require("./utils/prompt-command")(
NON_COMPILATION_CMD,
...process.argv
);
}
const yargs = require("yargs").usage(`webpack-cli ${
require("../package.json").version
}
Usage: webpack-cli [options]
webpack-cli [options] --entry <entry> --output <output>
webpack-cli [options] <entries...> --output <output>
webpack-cli <command> [options]
For more information, see https://webpack.js.org/api/cli/.`);
require("./config/config-yargs")(yargs);
// yargs will terminate the process early when the user uses help or version.
// This causes large help outputs to be cut short (https://github.com/nodejs/node/wiki/API-changes-between-v0.10-and-v4#process).
// To prevent this we use the yargs.parse API and exit the process normally
yargs.parse(process.argv.slice(2), (err, argv, output) => {
Error.stackTraceLimit = 30;
// arguments validation failed
if (err && output) {
console.error(output);
process.exitCode = 1;
return;
}
// help or version info
if (output) {
console.log(output);
return;
}
if (argv.verbose) {
argv["display"] = "verbose";
}
let options;
try {
options = require("./utils/convert-argv")(argv);
} catch (err) {
if (err.code === "MODULE_NOT_FOUND") {
const moduleName = err.message.split("'")[1];
let instructions = "";
let errorMessage = "";
if (moduleName === "webpack") {
errorMessage = `\n${moduleName} not installed`;
instructions = `Install webpack to start bundling: \u001b[32m\n $ npm install --save-dev ${moduleName}\n`;
if (
process.env.npm_execpath !== undefined &&
process.env.npm_execpath.includes("yarn")
) {
instructions = `Install webpack to start bundling: \u001b[32m\n $ yarn add ${moduleName} --dev\n`;
}
Error.stackTraceLimit = 1;
console.error(`${errorMessage}\n\n${instructions}`);
process.exitCode = 1;
return;
}
}
if (err.name !== "ValidationError") {
throw err;
}
const stack = ErrorHelpers.cleanUpWebpackOptions(err.stack, err.message);
const message = err.message + "\n" + stack;
if (argv.color) {
console.error(`\u001b[1m\u001b[31m${message}\u001b[39m\u001b[22m`);
} else {
console.error(message);
}
process.exitCode = 1;
return;
}
/**
* When --silent flag is present, an object with a no-op write method is
* used in place of process.stout
*/
const stdout = argv.silent ? { write: () => {} } : process.stdout;
function ifArg(name, fn, init) {
if (Array.isArray(argv[name])) {
if (init) init();
argv[name].forEach(fn);
} else if (typeof argv[name] !== "undefined") {
if (init) init();
fn(argv[name], -1);
}
}
function processOptions(options) {
// process Promise
if (typeof options.then === "function") {
options.then(processOptions).catch(function(err) {
console.error(err.stack || err);
// eslint-disable-next-line no-process-exit
process.exit(1);
});
return;
}
const firstOptions = [].concat(options)[0];
const statsPresetToOptions = require("webpack").Stats.presetToOptions;
let outputOptions = options.stats;
if (
typeof outputOptions === "boolean" ||
typeof outputOptions === "string"
) {
outputOptions = statsPresetToOptions(outputOptions);
} else if (!outputOptions) {
outputOptions = {};
}
ifArg("display", function(preset) {
outputOptions = statsPresetToOptions(preset);
});
outputOptions = Object.create(outputOptions);
if (Array.isArray(options) && !outputOptions.children) {
outputOptions.children = options.map((o) => o.stats);
}
if (typeof outputOptions.context === "undefined")
outputOptions.context = firstOptions.context;
ifArg("env", function(value) {
if (outputOptions.env) {
outputOptions._env = value;
}
});
ifArg("json", function(bool) {
if (bool) {
outputOptions.json = bool;
outputOptions.modules = bool;
}
});
if (typeof outputOptions.colors === "undefined")
outputOptions.colors = require("supports-color").stdout;
ifArg("sort-modules-by", function(value) {
outputOptions.modulesSort = value;
});
ifArg("sort-chunks-by", function(value) {
outputOptions.chunksSort = value;
});
ifArg("sort-assets-by", function(value) {
outputOptions.assetsSort = value;
});
ifArg("display-exclude", function(value) {
outputOptions.exclude = value;
});
if (!outputOptions.json) {
if (typeof outputOptions.cached === "undefined")
outputOptions.cached = false;
if (typeof outputOptions.cachedAssets === "undefined")
outputOptions.cachedAssets = false;
ifArg("display-chunks", function(bool) {
if (bool) {
outputOptions.modules = false;
outputOptions.chunks = true;
outputOptions.chunkModules = true;
}
});
ifArg("display-entrypoints", function(bool) {
outputOptions.entrypoints = bool;
});
ifArg("display-reasons", function(bool) {
if (bool) outputOptions.reasons = true;
});
ifArg("display-depth", function(bool) {
if (bool) outputOptions.depth = true;
});
ifArg("display-used-exports", function(bool) {
if (bool) outputOptions.usedExports = true;
});
ifArg("display-provided-exports", function(bool) {
if (bool) outputOptions.providedExports = true;
});
ifArg("display-optimization-bailout", function(bool) {
if (bool) outputOptions.optimizationBailout = bool;
});
ifArg("display-error-details", function(bool) {
if (bool) outputOptions.errorDetails = true;
});
ifArg("display-origins", function(bool) {
if (bool) outputOptions.chunkOrigins = true;
});
ifArg("display-max-modules", function(value) {
outputOptions.maxModules = +value;
});
ifArg("display-cached", function(bool) {
if (bool) outputOptions.cached = true;
});
ifArg("display-cached-assets", function(bool) {
if (bool) outputOptions.cachedAssets = true;
});
if (!outputOptions.exclude)
outputOptions.exclude = [
"node_modules",
"bower_components",
"components",
];
if (argv["display-modules"]) {
outputOptions.maxModules = Infinity;
outputOptions.exclude = undefined;
outputOptions.modules = true;
}
}
ifArg("hide-modules", function(bool) {
if (bool) {
outputOptions.modules = false;
outputOptions.chunkModules = false;
}
});
ifArg("info-verbosity", function(value) {
outputOptions.infoVerbosity = value;
});
ifArg("build-delimiter", function(value) {
outputOptions.buildDelimiter = value;
});
const webpack = require("webpack");
let lastHash = null;
let compiler;
try {
compiler = webpack(options);
} catch (err) {
if (err.name === "WebpackOptionsValidationError") {
if (argv.color)
console.error(
`\u001b[1m\u001b[31m${err.message}\u001b[39m\u001b[22m`
);
else console.error(err.message);
// eslint-disable-next-line no-process-exit
process.exit(1);
}
throw err;
}
if (argv.progress) {
const ProgressPlugin = require("webpack").ProgressPlugin;
new ProgressPlugin({
profile: argv.profile,
}).apply(compiler);
}
if (outputOptions.infoVerbosity === "verbose") {
if (argv.w) {
compiler.hooks.watchRun.tap("WebpackInfo", (compilation) => {
const compilationName = compilation.name ? compilation.name : "";
console.error("\nCompilation " + compilationName + " starting…\n");
});
} else {
compiler.hooks.beforeRun.tap("WebpackInfo", (compilation) => {
const compilationName = compilation.name ? compilation.name : "";
console.error("\nCompilation " + compilationName + " starting…\n");
});
}
compiler.hooks.done.tap("WebpackInfo", (compilation) => {
const compilationName = compilation.name ? compilation.name : "";
console.error("\nCompilation " + compilationName + " finished\n");
});
}
function compilerCallback(err, stats) {
if (!options.watch || err) {
// Do not keep cache anymore
compiler.purgeInputFileSystem();
}
if (err) {
lastHash = null;
console.error(err.stack || err);
if (err.details) console.error(err.details);
process.exitCode = 1;
return;
}
if (outputOptions.json) {
stdout.write(
JSON.stringify(stats.toJson(outputOptions), null, 2) + "\n"
);
} else if (stats.hash !== lastHash) {
lastHash = stats.hash;
if (stats.compilation && stats.compilation.errors.length !== 0) {
const errors = stats.compilation.errors;
if (errors[0].name === "EntryModuleNotFoundError") {
console.error(
"\n\u001b[1m\u001b[31mInsufficient number of arguments or no entry found."
);
console.error(
"\u001b[1m\u001b[31mAlternatively, run 'webpack(-cli) --help' for usage info.\u001b[39m\u001b[22m\n"
);
}
}
const statsString = stats.toString(outputOptions);
const delimiter = outputOptions.buildDelimiter
? `${outputOptions.buildDelimiter}\n`
: "";
if (statsString) stdout.write(`${statsString}\n${delimiter}`);
}
if (!options.watch && stats.hasErrors()) {
process.exitCode = 2;
}
}
if (firstOptions.watch || options.watch) {
const watchOptions =
firstOptions.watchOptions ||
options.watchOptions ||
firstOptions.watch ||
options.watch ||
{};
if (watchOptions.stdin) {
process.stdin.on("end", function(_) {
process.exit(); // eslint-disable-line
});
process.stdin.resume();
}
compiler.watch(watchOptions, compilerCallback);
if (outputOptions.infoVerbosity !== "none")
console.error("\nwebpack is watching the files…\n");
} else {
compiler.run((err, stats) => {
if (compiler.close) {
compiler.close((err2) => {
compilerCallback(err || err2, stats);
});
} else {
compilerCallback(err, stats);
}
});
}
}
processOptions(options);
});
})();
NON_COMPILATION_ARGS:
/**
* init 创建一份webpack配置文件
* migrate 进行webpack版本迁移
* add 往webpack配置文件中增加属性
* remove 往webpack配置文件中删除属性
* serve 运行webpack-server
* generate-loader 生成webpack loader代码
* generate-plugin 生成webpack plugin代码
* info 返回与本地环境相关的一些信息
*/
const NON_COMPILATION_ARGS = [
"init",
"migrate",
"add",
"remove",
"serve",
"generate-loader",
"generate-plugin",
"info",
];
const CONFIG_GROUP = "Config options:";
const BASIC_GROUP = "Basic options:";
const MODULE_GROUP = "Module options:";
const OUTPUT_GROUP = "Output options:";
const ADVANCED_GROUP = "Advanced options:";
const RESOLVE_GROUP = "Resolving options:";
const OPTIMIZE_GROUP = "Optimizing options:";
const DISPLAY_GROUP = "Stats options:";
const GROUPS = {
CONFIG_GROUP,
BASIC_GROUP,
MODULE_GROUP,
OUTPUT_GROUP,
ADVANCED_GROUP,
RESOLVE_GROUP,
OPTIMIZE_GROUP,
DISPLAY_GROUP,
};
const WEBPACK_OPTIONS_FLAG = "WEBPACK_OPTIONS";
module.exports = {
NON_COMPILATION_ARGS,
GROUPS,
WEBPACK_OPTIONS_FLAG,
};
prompt-command.js
// based on https://github.com/webpack/webpack/blob/master/bin/webpack.js
/**
* @param {string} command process to run
* @param {string[]} args commandline arguments
* @returns {Promise<void>} promise
*/
const runCommand = (command, args) => {
const cp = require("child_process");
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const executedCommand = cp.spawn(command, args, {
stdio: "inherit",
shell: true,
});
executedCommand.on("error", (error) => {
reject(error);
});
executedCommand.on("exit", (code) => {
if (code === 0) {
resolve();
} else {
reject();
}
});
});
};
const npmGlobalRoot = () => {
const cp = require("child_process");
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const command = cp.spawn("npm", ["root", "-g"]);
command.on("error", (error) => reject(error));
command.stdout.on("data", (data) => resolve(data.toString()));
command.stderr.on("data", (data) => reject(data));
});
};
const runWhenInstalled = (packages, pathForCmd, ...args) => {
const currentPackage = require(pathForCmd);
const func = currentPackage.default;
if (typeof func !== "function") {
throw new Error(
`@webpack-cli/${packages} failed to export a default function`
);
}
return func(...args);
};
module.exports = function promptForInstallation(packages, ...args) {
const nameOfPackage = "@webpack-cli/" + packages;
let packageIsInstalled = false;
let pathForCmd;
try {
const path = require("path");
const fs = require("fs");
pathForCmd = path.resolve(
process.cwd(),
"node_modules",
"@webpack-cli",
packages
);
if (!fs.existsSync(pathForCmd)) {
const globalModules = require("global-modules");
pathForCmd = globalModules + "/@webpack-cli/" + packages;
require.resolve(pathForCmd);
} else {
require.resolve(pathForCmd);
}
packageIsInstalled = true;
} catch (err) {
packageIsInstalled = false;
}
if (!packageIsInstalled) {
const path = require("path");
const fs = require("fs");
const readLine = require("readline");
const isYarn = fs.existsSync(path.resolve(process.cwd(), "yarn.lock"));
const packageManager = isYarn ? "yarn" : "npm";
const options = ["install", "-D", nameOfPackage];
if (isYarn) {
options[0] = "add";
}
if (packages === "init") {
if (isYarn) {
options.splice(1, 1); // remove '-D'
options.splice(0, 0, "global");
} else {
options[1] = "-g";
}
}
const commandToBeRun = `${packageManager} ${options.join(" ")}`;
const question = `Would you like to install ${packages}? (That will run ${commandToBeRun}) (yes/NO) : `;
console.error(
`The command moved into a separate package: ${nameOfPackage}`
);
const questionInterface = readLine.createInterface({
input: process.stdin,
output: process.stdout,
});
questionInterface.question(question, (answer) => {
questionInterface.close();
switch (answer.toLowerCase()) {
case "y":
case "yes":
case "1": {
runCommand(packageManager, options)
.then((_) => {
if (packages === "init") {
npmGlobalRoot()
.then((root) => {
const pathtoInit = path.resolve(
root.trim(),
"@webpack-cli",
"init"
);
return pathtoInit;
})
.then((pathForInit) => {
return require(pathForInit).default(...args);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
return;
}
pathForCmd = path.resolve(
process.cwd(),
"node_modules",
"@webpack-cli",
packages
);
return runWhenInstalled(packages, pathForCmd, ...args);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
break;
}
default: {
console.error(
`${nameOfPackage} needs to be installed in order to run the command.`
);
process.exitCode = 1;
break;
}
}
});
} else {
return runWhenInstalled(packages, pathForCmd, ...args);
}
};
2.命令行工具 yargs 介绍
提供命令和分组参数,动态生成 help 帮助信息
config-yargs:
const optionsSchema = require("../config/optionsSchema.json");
const { GROUPS } = require("../utils/constants");
const {
CONFIG_GROUP,
BASIC_GROUP,
MODULE_GROUP,
OUTPUT_GROUP,
ADVANCED_GROUP,
RESOLVE_GROUP,
OPTIMIZE_GROUP,
DISPLAY_GROUP,
} = GROUPS;
const nestedProperties = ["anyOf", "oneOf", "allOf"];
const resolveSchema = (schema) => {
let current = schema;
if (schema && typeof schema === "object" && "$ref" in schema) {
const path = schema.$ref.split("/");
for (const element of path) {
if (element === "#") {
current = optionsSchema;
} else {
current = current[element];
}
}
}
return current;
};
const findPropertyInSchema = (schema, property, subProperty) => {
if (!schema) return null;
if (subProperty) {
if (
schema[property] &&
typeof schema[property] === "object" &&
subProperty in schema[property]
) {
return resolveSchema(schema[property][subProperty]);
}
} else {
if (property in schema) return resolveSchema(schema[property]);
}
for (const name of nestedProperties) {
if (schema[name]) {
for (const item of schema[name]) {
const resolvedItem = resolveSchema(item);
const result = findPropertyInSchema(
resolvedItem,
property,
subProperty
);
if (result) return result;
}
}
}
return undefined;
};
const getSchemaInfo = (path, property, subProperty) => {
const pathSegments = path.split(".");
let current = optionsSchema;
for (const segment of pathSegments) {
if (segment === "*") {
current =
findPropertyInSchema(current, "additionalProperties") ||
findPropertyInSchema(current, "items");
} else {
current = findPropertyInSchema(current, "properties", segment);
}
if (!current) return undefined;
}
return findPropertyInSchema(current, property, subProperty);
};
module.exports = function(yargs) {
yargs
.help("help")
.alias("help", "h")
.version()
.alias("version", "v")
.options({
config: {
type: "string",
describe: "Path to the config file",
group: CONFIG_GROUP,
defaultDescription: "webpack.config.js or webpackfile.js",
requiresArg: true,
},
"config-register": {
type: "array",
alias: "r",
describe:
"Preload one or more modules before loading the webpack configuration",
group: CONFIG_GROUP,
defaultDescription: "module id or path",
requiresArg: true,
},
"config-name": {
type: "string",
describe: "Name of the config to use",
group: CONFIG_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
env: {
describe: "Environment passed to the config, when it is a function",
group: CONFIG_GROUP,
},
mode: {
type: getSchemaInfo("mode", "type"),
choices: getSchemaInfo("mode", "enum"),
describe: getSchemaInfo("mode", "description"),
group: CONFIG_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
context: {
type: getSchemaInfo("context", "type"),
describe: getSchemaInfo("context", "description"),
group: BASIC_GROUP,
defaultDescription: "The current directory",
requiresArg: true,
},
entry: {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("entry", "description"),
group: BASIC_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"no-cache": {
type: "boolean",
describe: "Disables cached builds",
group: BASIC_GROUP,
},
"module-bind": {
type: "string",
describe: "Bind an extension to a loader",
group: MODULE_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"module-bind-post": {
type: "string",
describe: "Bind an extension to a post loader",
group: MODULE_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"module-bind-pre": {
type: "string",
describe: "Bind an extension to a pre loader",
group: MODULE_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
output: {
alias: "o",
describe: "The output path and file for compilation assets",
group: OUTPUT_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"output-path": {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("output.path", "description"),
group: OUTPUT_GROUP,
defaultDescription: "The current directory",
requiresArg: true,
},
"output-filename": {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("output.filename", "description"),
group: OUTPUT_GROUP,
defaultDescription: "[name].js",
requiresArg: true,
},
"output-chunk-filename": {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("output.chunkFilename", "description"),
group: OUTPUT_GROUP,
defaultDescription:
"filename with [id] instead of [name] or [id] prefixed",
requiresArg: true,
},
"output-source-map-filename": {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("output.sourceMapFilename", "description"),
group: OUTPUT_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"output-public-path": {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("output.publicPath", "description"),
group: OUTPUT_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"output-jsonp-function": {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("output.jsonpFunction", "description"),
group: OUTPUT_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"output-pathinfo": {
type: "boolean",
describe: getSchemaInfo("output.pathinfo", "description"),
group: OUTPUT_GROUP,
},
"output-library": {
type: "array",
describe: "Expose the exports of the entry point as library",
group: OUTPUT_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"output-library-target": {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("output.libraryTarget", "description"),
choices: getSchemaInfo("output.libraryTarget", "enum"),
group: OUTPUT_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"records-input-path": {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("recordsInputPath", "description"),
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"records-output-path": {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("recordsOutputPath", "description"),
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"records-path": {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("recordsPath", "description"),
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
define: {
type: "string",
describe: "Define any free var in the bundle",
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
target: {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("target", "description"),
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
cache: {
type: "boolean",
describe: getSchemaInfo("cache", "description"),
default: null,
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
defaultDescription: "It's enabled by default when watching",
},
watch: {
type: "boolean",
alias: "w",
describe: getSchemaInfo("watch", "description"),
group: BASIC_GROUP,
},
"watch-stdin": {
type: "boolean",
alias: "stdin",
describe: getSchemaInfo("watchOptions.stdin", "description"),
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
},
"watch-aggregate-timeout": {
describe: getSchemaInfo("watchOptions.aggregateTimeout", "description"),
type: getSchemaInfo("watchOptions.aggregateTimeout", "type"),
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"watch-poll": {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("watchOptions.poll", "description"),
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
},
hot: {
type: "boolean",
describe: "Enables Hot Module Replacement",
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
},
debug: {
type: "boolean",
describe: "Switch loaders to debug mode",
group: BASIC_GROUP,
},
devtool: {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("devtool", "description"),
group: BASIC_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"resolve-alias": {
type: "string",
describe: getSchemaInfo("resolve.alias", "description"),
group: RESOLVE_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"resolve-extensions": {
type: "array",
describe: getSchemaInfo("resolve.alias", "description"),
group: RESOLVE_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"resolve-loader-alias": {
type: "string",
describe: "Setup a loader alias for resolving",
group: RESOLVE_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"optimize-max-chunks": {
describe: "Try to keep the chunk count below a limit",
group: OPTIMIZE_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"optimize-min-chunk-size": {
describe: getSchemaInfo(
"optimization.splitChunks.minSize",
"description"
),
group: OPTIMIZE_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"optimize-minimize": {
type: "boolean",
describe: getSchemaInfo("optimization.minimize", "description"),
group: OPTIMIZE_GROUP,
},
prefetch: {
type: "string",
describe: "Prefetch this request (Example: --prefetch ./file.js)",
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
provide: {
type: "string",
describe:
"Provide these modules as free vars in all modules (Example: --provide jQuery=jquery)",
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
"labeled-modules": {
type: "boolean",
describe: "Enables labeled modules",
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
},
plugin: {
type: "string",
describe: "Load this plugin",
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
requiresArg: true,
},
bail: {
type: getSchemaInfo("bail", "type"),
describe: getSchemaInfo("bail", "description"),
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
default: null,
},
profile: {
type: "boolean",
describe: getSchemaInfo("profile", "description"),
group: ADVANCED_GROUP,
default: null,
},
d: {
type: "boolean",
describe:
"shortcut for --debug --devtool eval-cheap-module-source-map --output-pathinfo",
group: BASIC_GROUP,
},
p: {
type: "boolean",
// eslint-disable-next-line quotes
describe:
'shortcut for --optimize-minimize --define process.env.NODE_ENV="production"',
group: BASIC_GROUP,
},
silent: {
type: "boolean",
describe: "Prevent output from being displayed in stdout",
},
json: {
type: "boolean",
alias: "j",
describe: "Prints the result as JSON.",
},
progress: {
type: "boolean",
describe: "Print compilation progress in percentage",
group: BASIC_GROUP,
},
color: {
type: "boolean",
alias: "colors",
default: function supportsColor() {
return require("supports-color").stdout;
},
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Force colors on the console",
},
"no-color": {
type: "boolean",
alias: "no-colors",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Force no colors on the console",
},
"sort-modules-by": {
type: "string",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Sorts the modules list by property in module",
},
"sort-chunks-by": {
type: "string",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Sorts the chunks list by property in chunk",
},
"sort-assets-by": {
type: "string",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Sorts the assets list by property in asset",
},
"hide-modules": {
type: "boolean",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Hides info about modules",
},
"display-exclude": {
type: "string",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Exclude modules in the output",
},
"display-modules": {
type: "boolean",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Display even excluded modules in the output",
},
"display-max-modules": {
type: "number",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Sets the maximum number of visible modules in output",
},
"display-chunks": {
type: "boolean",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Display chunks in the output",
},
"display-entrypoints": {
type: "boolean",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Display entry points in the output",
},
"display-origins": {
type: "boolean",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Display origins of chunks in the output",
},
"display-cached": {
type: "boolean",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Display also cached modules in the output",
},
"display-cached-assets": {
type: "boolean",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Display also cached assets in the output",
},
"display-reasons": {
type: "boolean",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Display reasons about module inclusion in the output",
},
"display-depth": {
type: "boolean",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Display distance from entry point for each module",
},
"display-used-exports": {
type: "boolean",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe:
"Display information about used exports in modules (Tree Shaking)",
},
"display-provided-exports": {
type: "boolean",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Display information about exports provided from modules",
},
"display-optimization-bailout": {
type: "boolean",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe:
"Display information about why optimization bailed out for modules",
},
"display-error-details": {
type: "boolean",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Display details about errors",
},
display: {
type: "string",
choices: [
"",
"verbose",
"detailed",
"normal",
"minimal",
"errors-only",
"none",
],
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Select display preset",
},
verbose: {
type: "boolean",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Show more details",
},
"info-verbosity": {
type: "string",
default: "info",
choices: ["none", "info", "verbose"],
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe:
"Controls the output of lifecycle messaging e.g. Started watching files...",
},
"build-delimiter": {
type: "string",
group: DISPLAY_GROUP,
describe: "Display custom text after build output",
},
});
};
3.webpack-cli 使用 args 分析
参数分组(config/config-args.js)将命令划分为了 9 类:
Config options: 配置相关参数(文件名称、运行参数等)Basic options: 基础参数(entry 设置、debug 模式设置、watch 监听设置、devtool 设置)Module options: 模块参数,给 loader 设置扩展Output options: 输出参数(输出路径、输出文件名称)Advanced options: 高级用法(记录设置、缓存设置、监听频率、bail 等)Resolving options: 解析参数(alias 和 解析的文件后缀设置)Optimizing options: 优化参数Stats options: 统计参数options: 通用参数(帮助命令、版本信息等)
TIP
webpack-cli 执行的结果
webpack-cli 配置文件和命令行参数进行转换最终胜出配置选项参数 options
最终会根据配置参数实例化 webpack 对象,然后执行构建流程
Tapable 插件架构与 Hooks 设计
- 2020.08.16
webpack 的本质是什么?
可以理解为 webpack 是一种基于事件流的编程范例,一系列的插件运行。
其中核心对象 Complier 继承 Tapable,Complation 也是继承 Tapable。
Tapable 是什么?
Tapable是一个类似于Node.js的EventEmitter插件库,主要是控制钩子函数的发布与订阅,控制着webpack的插件系统。
Tapable 库暴露了很多的 Hook(钩子)类,为插件的挂载提供了钩子
const {
Tapable,
SyncHook, // 同步钩子
SyncBailHook, // 同步熔断钩子
SyncWaterfallHook, // 同步流水钩子
SyncLoopHook, // 同步循环钩子
AsyncParallelHook, // 异步并发钩子
AsyncParallelBailHook, // 异步并发熔断钩子
AsyncSeriesHook, // 异步串行钩子
AsyncSeriesBailHook, // 异步串行熔断钩子
AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook, // 异步串行流水钩子
} = require("tapable");
hooks 类型:
| type | function |
|---|---|
Hook | 所有钩子的后缀 |
Waterfall | 同步方法,但是他会传值给下一个函数 |
Bail | 熔断,当函数有任何返回值,则在当前执行函数停止 |
Loop | 监听函数返回 true 表示循环,返回 undefined 表示结束循环 |
Sync | 同步方法 |
AsyncSeries | 异步串行钩子 |
AsyncParallel | 异步并行执行钩子 |
Tapable 的使用————new Hook(新建钩子)
Tapable 暴露出来的都是类方法,我们需要 new 一个类方法获得我们需要的钩子。class 接收数组参数 options,非必传。类方法会根据传参,接收同样数量的参数。
const hook1 = new SyncHook([arg1, arg2, arg3]);
Tapable 的使用————钩子的绑定与执行
Tapable 提供了同步和异步的绑定钩子的方法,并且他们都有绑定事件和执行事件对应的方法。
| Async* | Sync* |
|---|---|
| 绑定: tapAsync、tapPromise、tap | 绑定: tap |
| 执行: callAsync、promise | 执行: call |
Tapable 的使用————hook 基本用法示例
const hook1 = new SyncHook(["arg1", "arg2", "arg3"]);
// 绑定事件到webpack事件流
hook1.tap("hook1", (arg1, arg2, arg3) => console.log(arg1, arg2, arg3));
// 执行绑定的事件
hook1.call(1, 2, 3);
Tapable 的使用————实际例子演示
定义一个 Car 方法,在内部 hook 上新建钩子。分别是同步钩子 accelerate、brake(accelerate 接收一个参数)和异步钩子calculateRoutes。
使用钩子对应的绑定和执行方法。
calculateRoutes使用tapPromise可以返回一个promise对象。
// Car.js
const { SyncHook, AsyncSeriesHook } = require("tapable");
class Car {
constructor() {
this.hooks = {
accelerate: new SyncHook(["newspeed"]),
brake: new SyncHook(),
calculateRoutes: new AsyncSeriesHook(["source", "trget", "routesList"]),
};
}
}
const myCar = new Car();
// 绑定同步钩子
myCar.hooks.brake.tap("WarningLampPlugin", () =>
console.log("WarningLampPlugin")
);
// 绑定同步钩子 并传参
myCar.hooks.accelerate.tap("LoggerPlugin", (newSpeed) =>
console.log(`Accelerating to ${newSpeed}`)
);
//
myCar.hooks.calculateRoutes.tapPromise(
"calculateRoutes tapPromise",
(source, trget, routesList, callback) => {
console.log("source", source);
return new Promise((resolve, rej) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`tapPromise to ${source} ${trget} ${routesList}`);
resolve();
}, 1000);
});
}
);
myCar.hooks.brake.call();
myCar.hooks.accelerate.call(10);
console.time("cost");
// 执行异步钩子
myCar.hooks.calculateRoutes.promise("Async", "hook", "demo").then(
() => {
console.timeEmd("cost");
},
(err) => {
console.error(err);
console.timeEmd("cost");
}
);
Tapable 是如何和 webpack 关联起来的
- 2020.08.17
// webpack.js
/**
* @param {WebpackOptions} options options object
* @param {function(Error=, Stats=): void=} callback callback
* @returns {Compiler | MultiCompiler} the compiler object
*/
const webpack = (options, callback) => {
const webpackOptionsValidationErrors = validateSchema(
webpackOptionsSchema,
options
);
if (webpackOptionsValidationErrors.length) {
throw new WebpackOptionsValidationError(webpackOptionsValidationErrors);
}
let compiler;
if (Array.isArray(options)) {
compiler = new MultiCompiler(
Array.from(options).map((options) => webpack(options))
);
} else if (typeof options === "object") {
options = new WebpackOptionsDefaulter().process(options);
compiler = new Compiler(options.context);
compiler.options = options;
new NodeEnvironmentPlugin({
infrastructureLogging: options.infrastructureLogging,
}).apply(compiler);
// 这里对应的就是webpack.config.js中对应的plugins数组执行
if (options.plugins && Array.isArray(options.plugins)) {
for (const plugin of options.plugins) {
if (typeof plugin === "function") {
plugin.call(compiler, compiler);
} else {
plugin.apply(compiler);
}
}
}
compiler.hooks.environment.call();
compiler.hooks.afterEnvironment.call();
compiler.options = new WebpackOptionsApply().process(options, compiler);
} else {
throw new Error("Invalid argument: options");
}
if (callback) {
if (typeof callback !== "function") {
throw new Error("Invalid argument: callback");
}
if (
options.watch === true ||
(Array.isArray(options) && options.some((o) => o.watch))
) {
const watchOptions = Array.isArray(options)
? options.map((o) => o.watchOptions || {})
: options.watchOptions || {};
return compiler.watch(watchOptions, callback);
}
compiler.run(callback);
}
return compiler;
};
模拟一个自定义的 complier
class Complier {
constructor(){
this.hooks = {
accelerate: new SyncHook(['newspeed']),
brake: new SyncHook(),
calculateRoutes: new AsyncSeriesHook(['source', 'trget', 'routesList'])
}
}
run(){
this.accelerate(10);
this.break;
this.calculateRoutes('Async', 'Hook', 'Demo');
}
accelerate(speed){
this.hooks.accelerate.call(speed);
}
break(){
this.hooks.brake.call();
}
calculateRoutes(){
this.hooks.calculateRoutes.promise(..arguments).then(()=>{
}, err=>{
console.error(err);
})
}
}
module.exports = Complier;
根据 Complier 编写一个简易的自定义插件
通过上面的分析我们知道自定义插件需要接收一个 complier 对象参数,内部需要有一个 apply 方法。
const complier = require('./complier');
class MyFirstPlugin = {
constructor(){
}
apply(complier){
complier.hooks.break.tap("WarningLampPlugin",()=> console.log('WarningLampPlugin'));
complier.hooks.accelerate.tap("LoggerPlugin", (newSpeed)=>{
console.log(`Accelerate to ${newSpeed}`);
})
complier.hooks.calculateRoutes.tapPromise("calculateRoutes tapAsync",(source, target, routesList)=>{
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log(`tapPromise to ${source} ${target} ${routesList}`);
resolve();
},1000)
});
})
}
}
模拟插件的执行
const myPlugin = new MyFirstPlugin();
const options = {
plugins: [myPlugin],
};
const complier = new Complier();
for (const plugin of options.plugins) {
if (typeof plugin === "function") {
plugin.call(compiler, compiler);
} else {
plugin.apply(compiler);
}
}
complier.run();
webpack 流程细剖————准备篇
- 2020.08.17
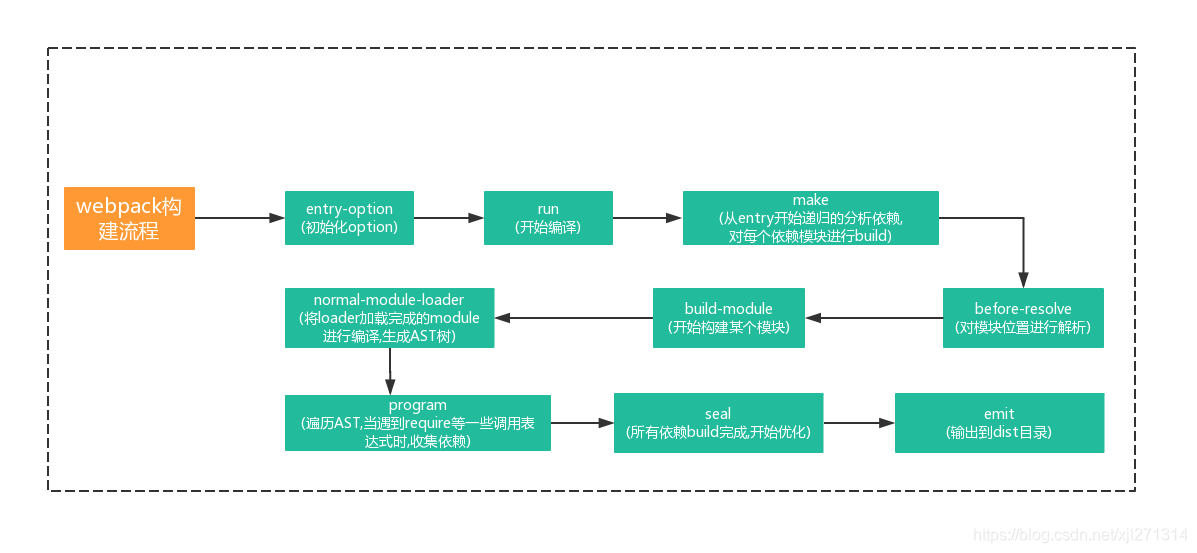
模块构建和 chunk 生成阶段
- 2020.08.17
ModuleFactory
- NormalModuleFactory
指那些通过普通的
module.exports导出的模块。
- ContextModuleFactory
路径模块之类的。
Module 的类型
NormalModule普通模块
Build 通过:
使用
loader-runner运行 loaders通过
Parser解析(内部是 acron)ParserPlugins添加依赖
ContextModule路径模块
'./src/a'
ExternalModule外部模块
module.exports = Jquery
DelegatedModule
manifest
MultiModule
entry: ['a', 'b']
chunk 生成算法
webpack先将entry中对应的module都生成一个新的chunk- 遍历
module的依赖列表,将依赖的module也加入到chunk中 - 如果一个依赖
module是动态引入的模块,那么就会根据这个module创建一个新的chunk,继续遍历依赖 - 重复上面的过程,知道得到所有的
chunks
webpack 流程篇————文件生成
- 2020.08.18
TIP
这里有一个点,文件生成的Hash值是在seal阶段生成的。
调用的是Complation.js中的this.createHash方法。
实战篇————动手编写一个简易的 webpack
- 2020.08.18
知识点回顾:
webpack打包出来的是一个IIFE(匿名闭包)。modules是一个数组,每一项是一个模块初始化函数。__webpack__require用来加载模块,返回module.exports。通过WEBPACK_REQUIRE_METHOD(0)来启动程序。
功能需求:
可以将 ES6 预发转化成 ES5 的语法。
- 通过
babylon生成 AST 树 - 通过
babel-core将 AST 重新生成源码
- 通过
可以分析模块之间的依赖关系
- 通过
babel-traverse的ImportDeclaration方法获取依赖属性
- 通过
生成的 JS 文件可以在浏览器中运行。
完整示例
Loader 的链式调用和执行顺序
- 2020.08.19
loader 只是一个导出为函数的 Javascript 函数,我们知道定义的 loader 是从右往左依次执行的。
module.exports = function(source) {
return source;
};
loader 是串行执行的, loader 的执行顺序为: postcss-loader -> scss-loader -> css-loader -> style-loader
module.exports = {
...,
module:{
rule: [
test: /\.scss$/,
use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader', 'scss-loader','postcss-loader']
]
}
}
loader 的实现方式和我们之前接触的 compose 函数的思想是一致的。
compose 函数
compose 函数接收一个参数返回一个组合后的复合函数,下一个函数会以上个函数的返回值作为参数
function compose() {
var args = [...arguments];
return function(initArg) {
var result = initArg;
for (var i = args.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result = args[i](result);
}
return result;
};
}
// 调用ReduceRight()
function compose1() {
var args = [].slice.call(arguments);
return function(initArg) {
return args.reduceRight(function(init, current) {
return current(init);
}, initArg);
};
}
使用 webpack-cli 创建 loader
webpack - cli - loader;
使用 loader-runner 高效进行 loader 的调式
- 2020.08.20
loader-runner允许你在不安装webpack的情况下运行loaders
作用:
- 作为 webpack 的依赖,webpack 中使用它执行 loader
- 进行 loader 的开发和测试。
import { runLoaders } from "loader-runner";
runLoaders(
{
resource: "/abs/path/to/file.txt?query",
// String: Absolute path to the resource (optionally including query string)
loaders: ["/abs/path/to/loader.js?query"],
// String[]: Absolute paths to the loaders (optionally including query string)
// {loader, options}[]: Absolute paths to the loaders with options object
context: { minimize: true },
// Additional loader context which is used as base context
readResource: fs.readFile.bind(fs),
// A function to read the resource
// Must have signature function(path, function(err, buffer))
},
function(err, result) {
// err: Error?
// result.result: Buffer | String
// The result
// result.resourceBuffer: Buffer
// The raw resource as Buffer (useful for SourceMaps)
// result.cacheable: Bool
// Is the result cacheable or do it require reexecution?
// result.fileDependencies: String[]
// An array of paths (files) on which the result depends on
// result.contextDependencies: String[]
// An array of paths (directories) on which the result depends on
}
);
开发一个 raw-loader
// raw-loader \u2028: 行分隔符 \u2029: 段落分隔符
module.exports = function(source){
const json = JSON.stringify(source).replace(/\u2028/g, '\\u2028').replace(/\u2029/g, '\\u2029')
return `export default ${json}`;
}
// run-loader.js
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const { runLoaders } = require('loader-runner');
runLoaders(
{
resource: './demo.txt',
loaders: [path.resolve(__dirname, './loaders/raw-loader')],
readResource: fs.readFile.bind(fs)
},
(err, result)=> err ? console.error(err) : console.log(result)
);
// 运行
node run-loader.js
// 结果
{
result: ['export defualt footbar'],
resourceBuffer: <Buffer 66 6f 6f 62 61 72>,
cacheable: true,
fileDependencies: ['./src/demo.txt'],
contextDependencies: []
}
更复杂的 loader 开发场景
实际的 loader 开发过程中往往涉及到很多,比如 loader 的参数获取、loader 内部的异常处理
通过 loader-utils 的 getOptions 方法获取参数
const loaderUtils = require("loader-utils");
module.exports = function(source) {
const { name } = loaderUtils.getOptions(this);
};
loader 内部的异常处理
loader 内直接通过
throw抛出,通过this.callback传递错误。
this.callback(
err: Error | null,
content: string | Buffer,
sourceMap?: sourceMap,
meta?: any
);
loader 的异步处理
通过
this.async来返回一个异步函数(第一个参数是Error,第二个参数是处理的结果)
module.exports = function(input) {
const callback = this.async();
// No callback -> return synchronous results
// if callback ....
callback(null, input + input);
};
在 loader 中使用缓存
webpack 中默认是开启 loader 缓存的(可以使用
this.cacheable关掉缓存)。
缓存的条件:
loader的结果在相同的输入下有明确的输出,有依赖的loader无法使用缓存。
在 loader 中如何进行文件输出
loader 中通过
this.emitFile进行文件写入
const loaderUtils = require("loader-utils");
module.exports = function(source) {
const url = loaderUtils.interpolateName(this, "[name].[ext]", {
source,
});
this.emitFile(path.join(__dirname, url), source);
const path = `__webpack_public_path__+${JSON.stringify(url)}`;
return `export default ${path}`;
};
开发一个自动合成雪碧图的 loader
- 2020.08.20
准备知识:如何将两张图片合成一张图片?
使用 spritesmith(https://www.npmjs.com/package/spritesmith)
const Spritesmith = require('spritesmith ');
const path = require('path');
const fs = require('fs');
module.exports = {
const callback = this.async();
const imgs = source.match(/url\((\s*)\?__sprite/g);
const matchedImgs = [];
for(let i = 0; i< imgs.length; i++){
const img = imgs[i].match(/url\((\s*)\?__sprite/)[1];
matchedImgs.push(path.join(__dirname, img))
}
Spritesmith.run({
src: matchedImgs,
}, (err, result)=>{
fs.writeFileSync(path.join(process.cwd(), 'dist/sprite.jpg'), result.image);
source = source.replace(/url\((\s*)\?__sprite/g), (match)=>{
return `url("dist/sprite.jpg")`;
})
fs.writeFileSync(path.join(process.cwd(), 'dist/index.css'), source);
callback(null, source);
}
});
}
插件基本结构介绍
- 2020.08.20
用于处理除了 loader 以外的功能,没有像 loader 一样的独立运行环境,只能在 webpack 中运行。
class MyPlugin {
// 插件的名称
apply(compiler) {
// 必须的apply方法
compiler.hooks.done.tap("My Plugin", (stats) => {
// 触发的hooks
// do something ...
});
}
}
module.exports = MyPlugin;
// 插件的使用
plugins: [new MyPlugin()];
动手实现一个 loader 之简易的 jsx-px2rem
- 2020.09.08
此 loader 用于将 jsx 中的 style 中的 px 转换为 rem。
jsx-px2rem-loader.js:
import regRules from "./reg";
import _ from "lodash"; // lodash是一个js工具库,特别方便建议各位去了解一下
module.exports = function(source) {
// webpack中默认是开启loader缓存的(可以使用this.cacheable关掉缓存)。
if (this.cacheable) {
this.cacheable();
}
let backUp = source;
// style={{marginRight: '1px'}} => style={{marginRight: '0.01rem'}}
if (regRules.pxReg.test(backUp)) {
backUp = backUp.replace(regRules.pxReg, (px) => {
let val = px.replace(regRules.numReg, (num) => {
return num / 100;
});
val = val.replace(/px$/, "rem");
return val;
});
}
// marginRight: 1 => marginRight: '0.01rem'
_.each(regRules.styleReg, (reg, styleName) => {
if (reg.test(backUp)) {
backUp = backUp.replace(reg, (val) => {
return val.replace(regRules.numReg, (num) => {
return `"${num / 100}rem"`;
});
});
}
});
// img标签 width: 1 => style={{width: '0.01rem'}}
_.each(regRules.imgReg, (reg, styleName) => {
if (reg.test(backUp)) {
backUp = backUp.replace(reg, (val) => {
let style = "";
val.replace(regRules.numReg, (num) => {
style = `${num / 100}rem`;
});
return `style={{${styleName}:"${style}"}}`;
});
}
});
return backUp;
};
reg.js:
// 匹配jsx中的px 如 1px
const pxReg = /\b(\d+(\.\d+)?)px\b/g;
// 匹配jsx中 缩写形式的style 如:marginRight: 1
const styleReg = {
marginTop: /\bmarginTop(?:\s+):(?:\s+)?(\d+)/g,
marginRight: /\bmarginRight(?:\s+)?:(?:\s+)?(\d+)/g,
marginBottom: /\bmarginBottom(?:\s+)?:(?:\s+)?(\d+)/g,
marginLeft: /\bmarginLeft(?:\s+)?:(?:\s+)?(\d+)/g,
fontSize: /\bfontSize(?:\s+)?:(?:\s+)?(\d+)/g,
paddingTop: /\bpaddingTop(?:\s+)?:(?:\s+)?(\d+)/g,
paddingRight: /\bpaddingRight(?:\s+)?:(?:\s+)?(\d+)/g,
paddingBottom: /\bpaddingBottom(?:\s+)?:(?:\s+)?(\d+)/g,
paddingLeft: /\bpaddingLeft(?:\s+)?:(?:\s+)?(\d+)/g,
};
// 匹配img 中的行内样式 width: '20'
const imgReg = {
height: /\bheight(?:\s+)?=(?:\s+)?(\'||\")?(\d+)?=(\'||\")?/g,
width: /\bwidth(?:\s+)?=(?:\s+)?(\'||\")?(\d+)?=(\'||\")?/g,
};
// 匹配数字
const numReg = /(\d+)/g;
export default {
pxReg,
styleReg,
imgReg,
numReg,
};
config.js:
import path from 'path'
...
chainWebpack(config){
config.module
.rule('jsx-px2rem-loader')
.test(/\.js$/)
.exclude
.add([path.resolve('../src/pages/.umi'), path.resolve('node_modules')])
.end()
.use('../loader/jsx-px2rem-loader')
.loader(path.join(__dirname, '../loader/jsx-px2rem-loader'));
}
← Babel 前端轻量自动化构建方案 →